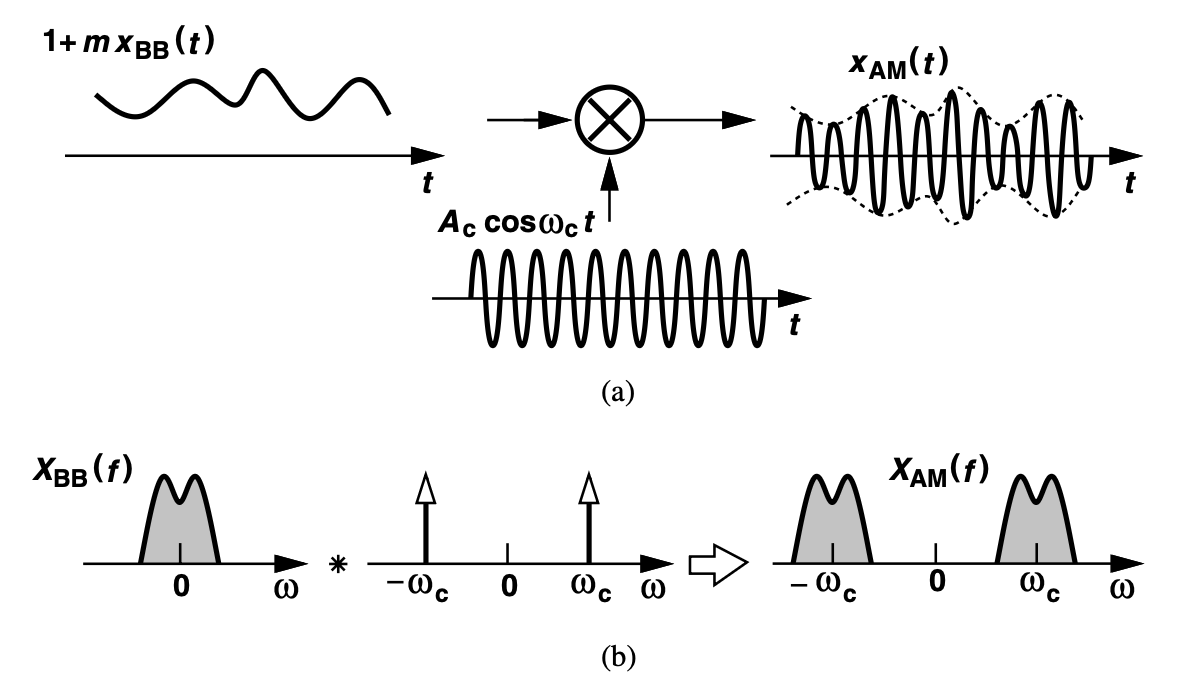
Communication¶
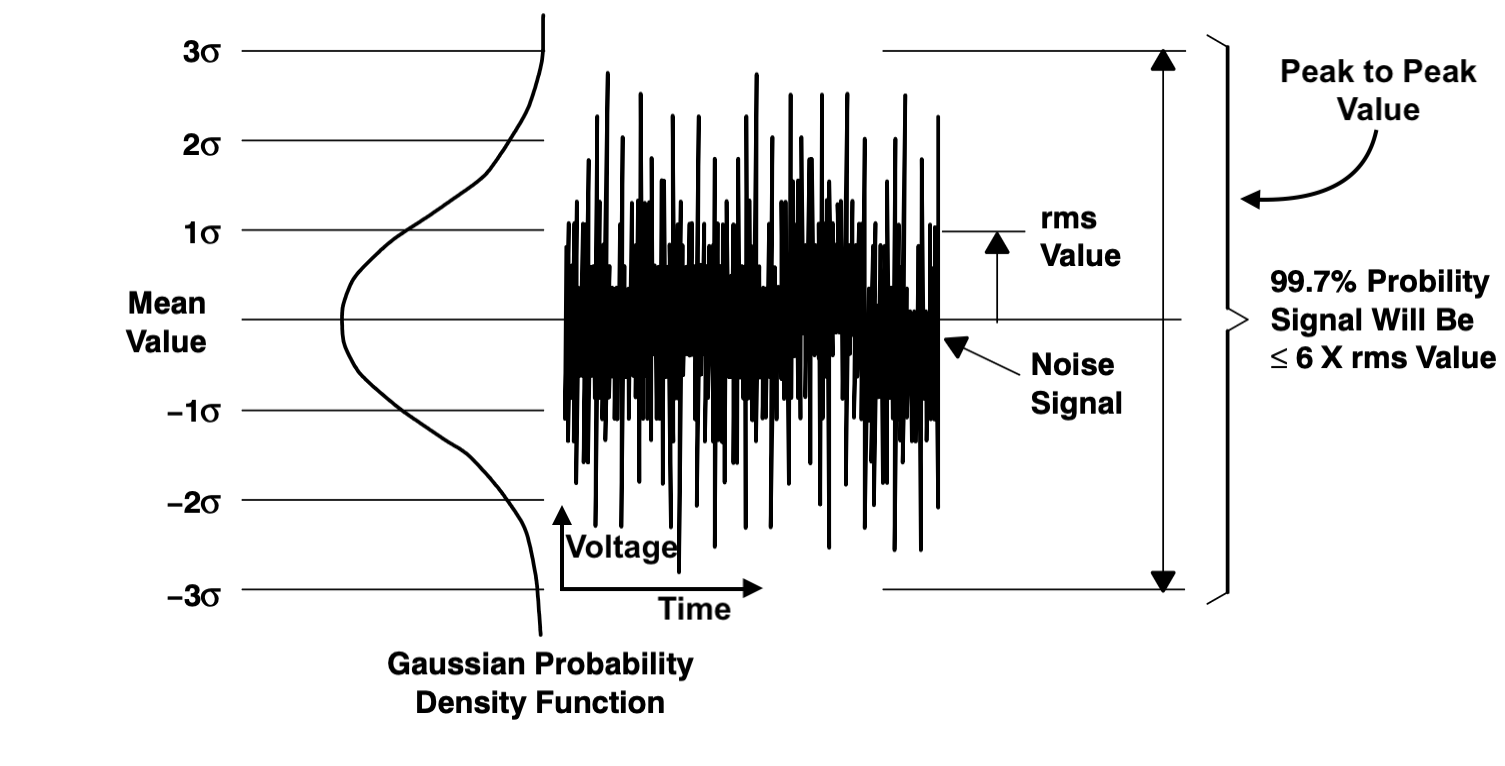
Noise figure in RF systems quantifies how much a component or circuit degrades the signal-to-noise ratio as a signal passes through it.
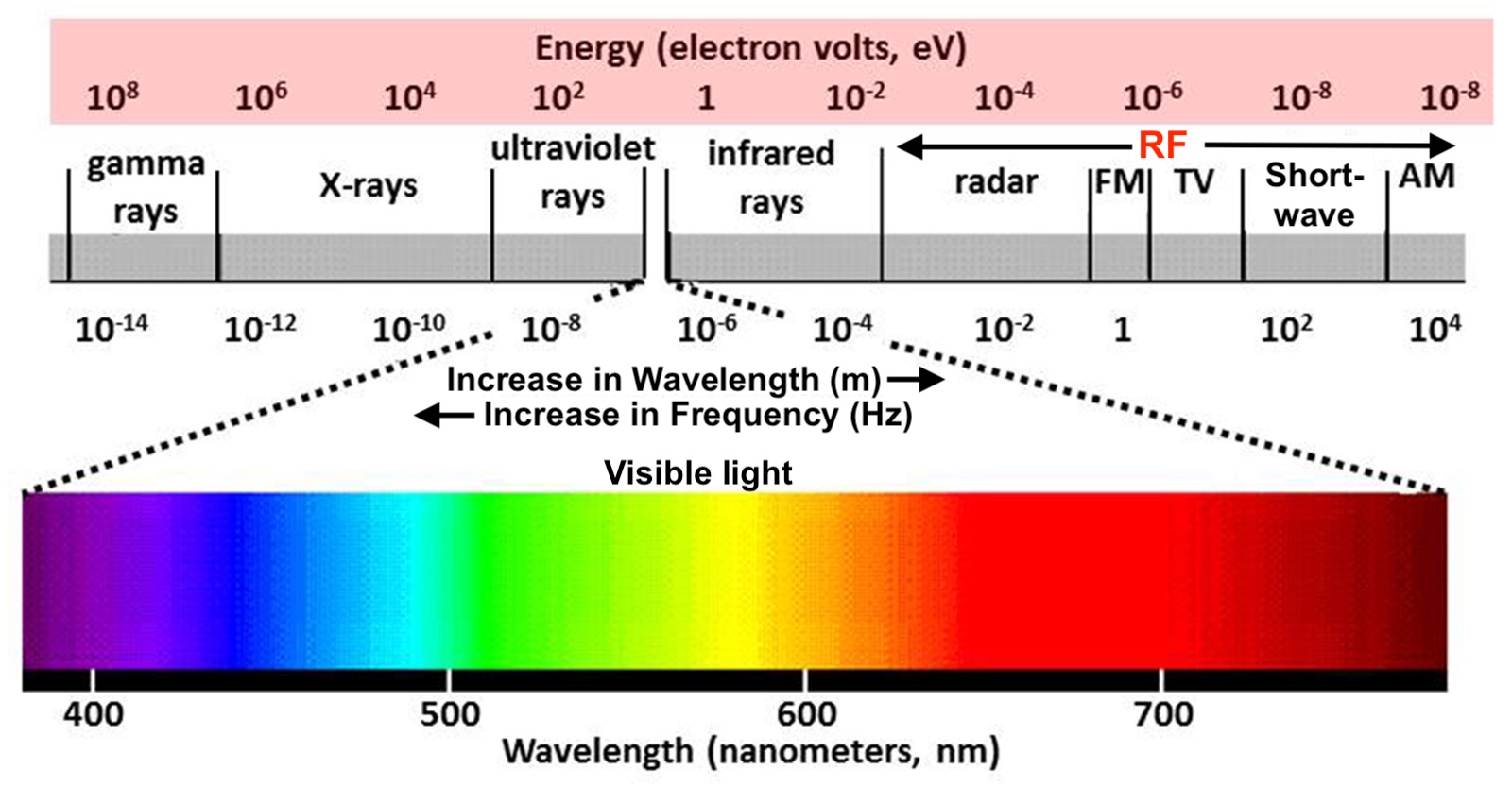
Feedback systems use a portion of the output signal to influence the input, improving stability, accuracy, and performance of electrical and control systems.
The Shannon–Hartley theorem defines the maximum achievable data rate of a communication channel based on bandwidth and signal-to-noise ratio.
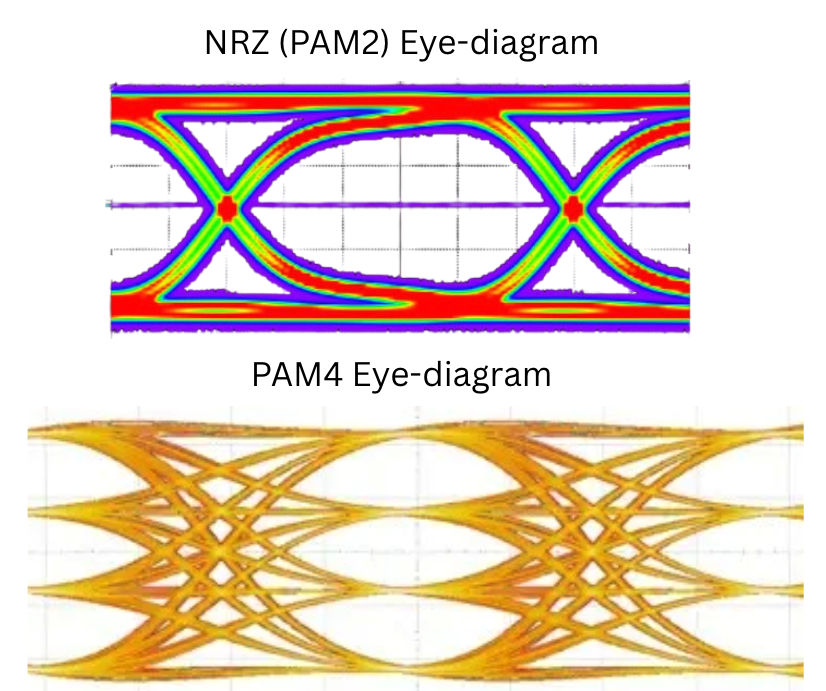
An eye diagram visually represents signal quality in digital communication, while bit error rate quantifies the frequency of bit errors in a data stream.
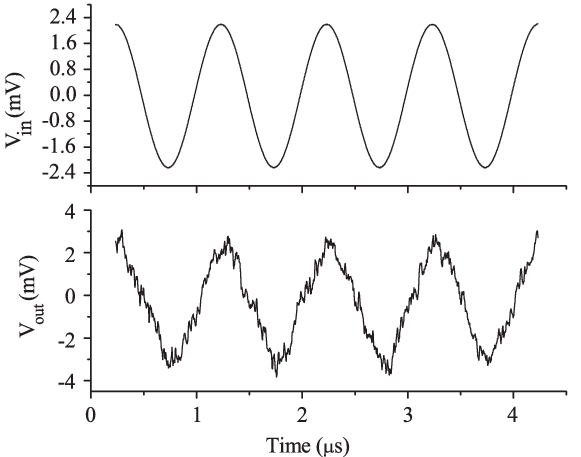
Noise figure in RF systems quantifies how much a component or circuit degrades the signal-to-noise ratio as a signal passes through it.
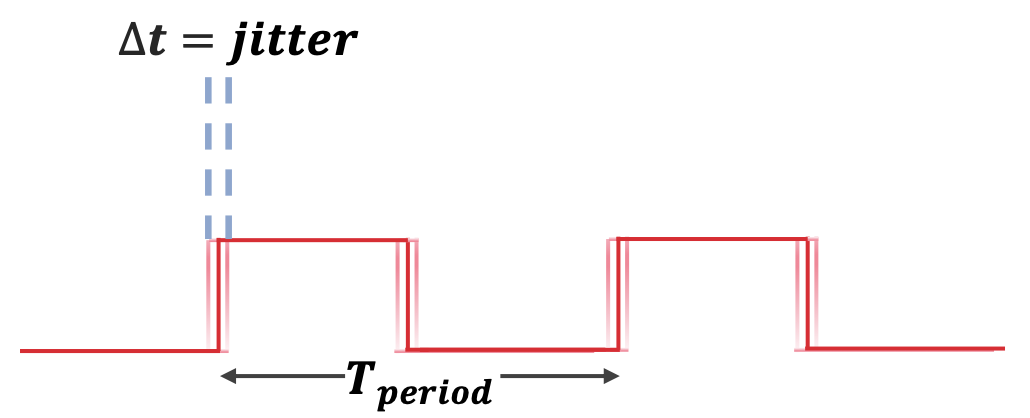
Jitter is the short-term variation in the timing of a signal’s edges relative to their ideal positions in time.
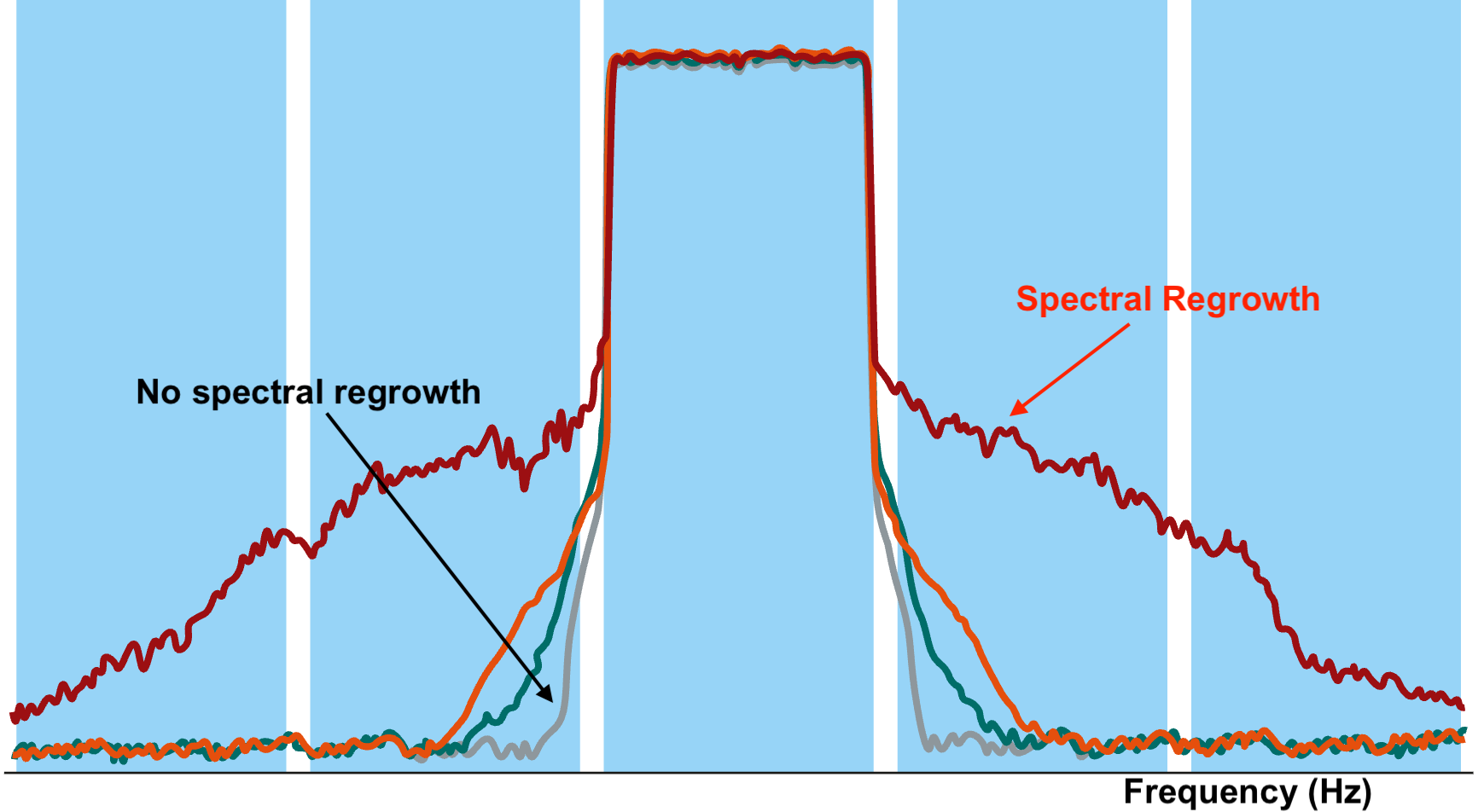
Spectral regrowth is the spreading of a signal’s spectrum caused by nonlinearities in RF power amplifiers and other active devices.
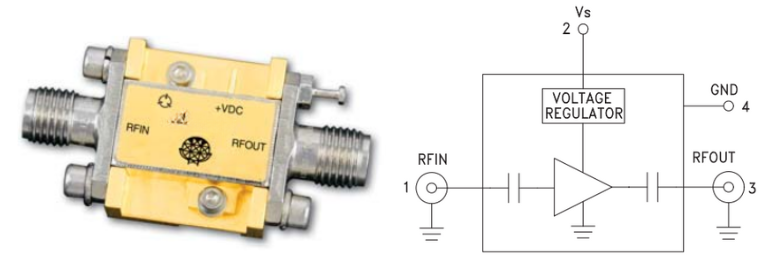
A low noise amplifier in RF is designed to amplify weak signals while adding minimal noise, improving overall receiver sensitivity.
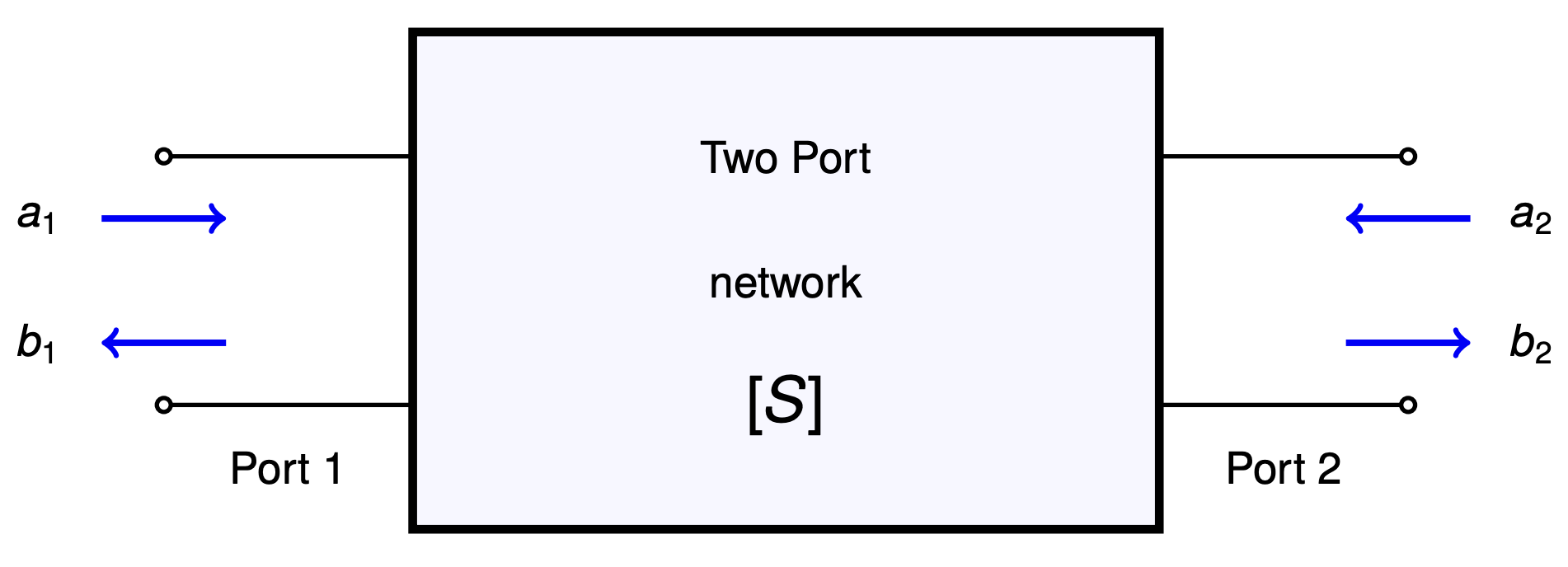
Noise figure in RF systems quantifies how much a component or circuit degrades the signal-to-noise ratio as a signal passes through it.
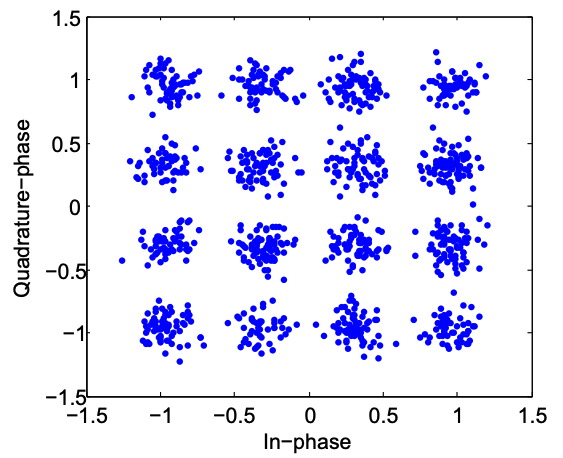
A constellation diagram in RF represents digitally modulated signals by plotting symbol amplitude and phase on an I–Q plane.
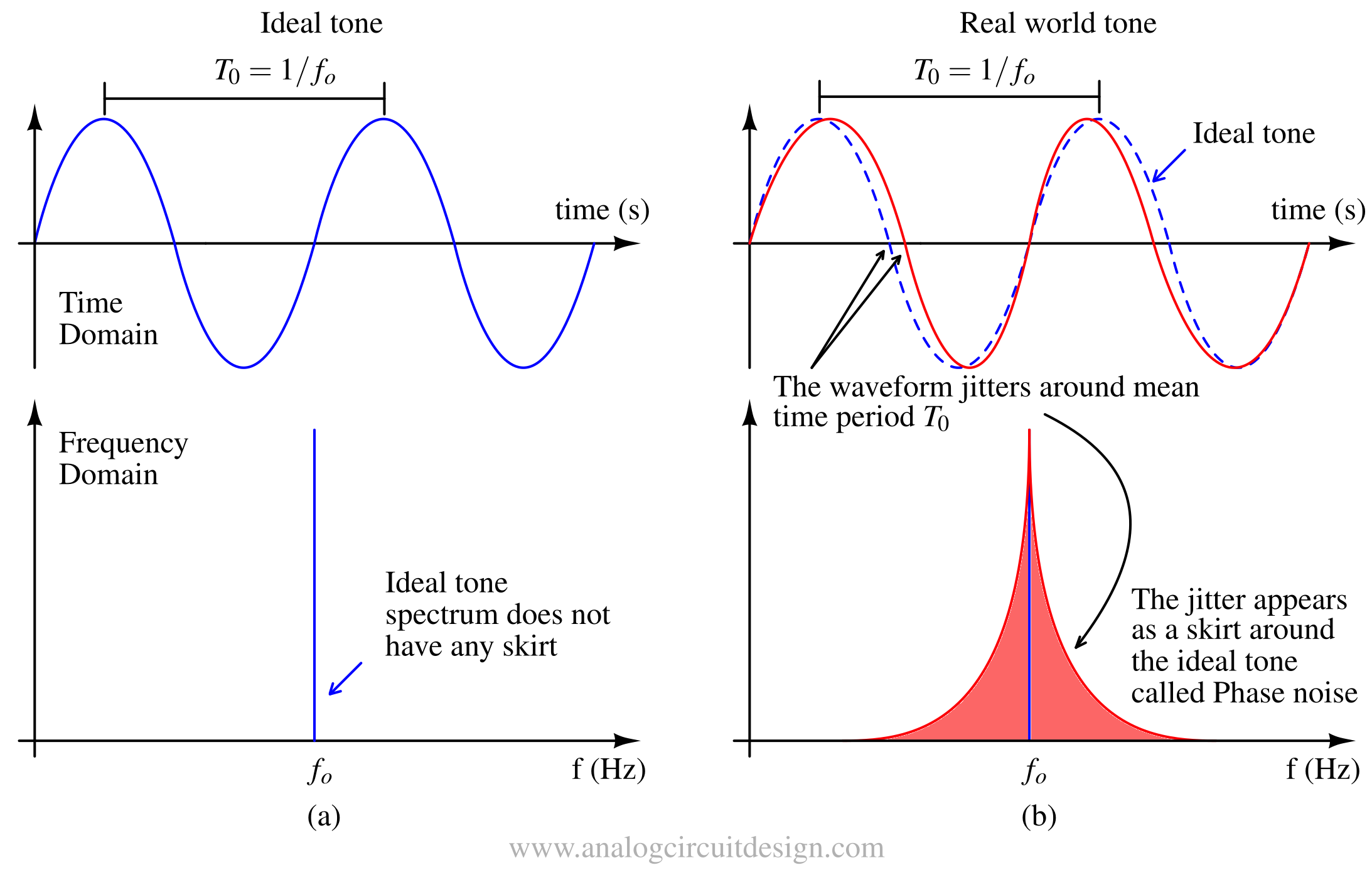
Phase noise represents the short-term frequency instability of an oscillator, appearing as noise sidebands around the carrier signal.