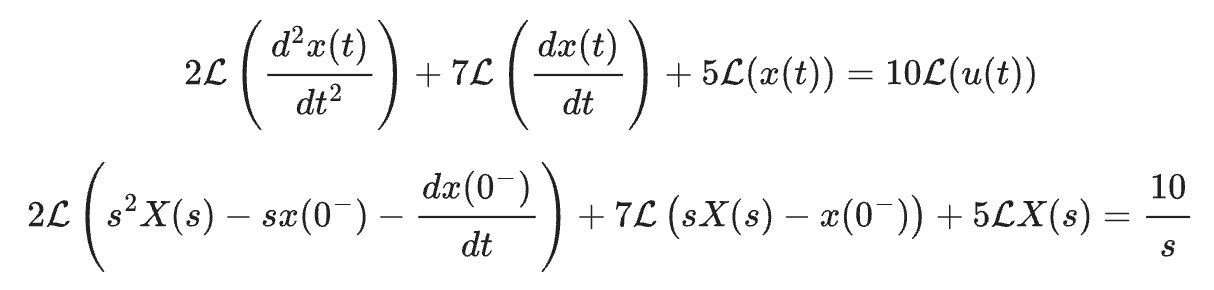Control¶
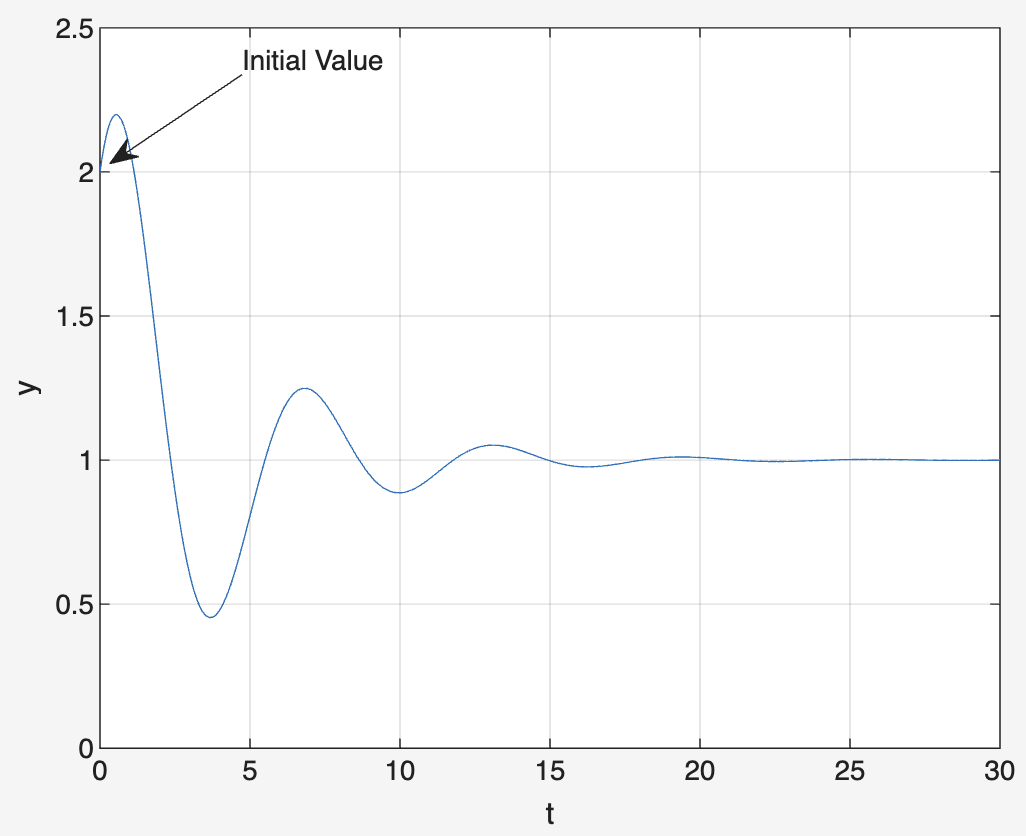
The initial value theorem relates the behavior of a function as time approaches zero to its Laplace transform, helping analyze system response at the start.
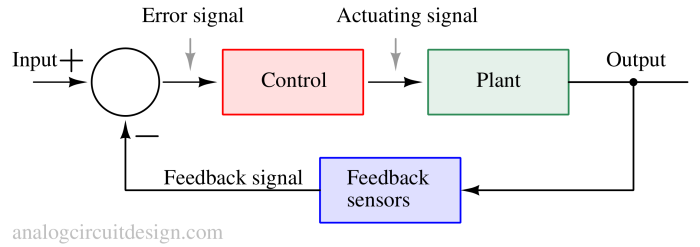
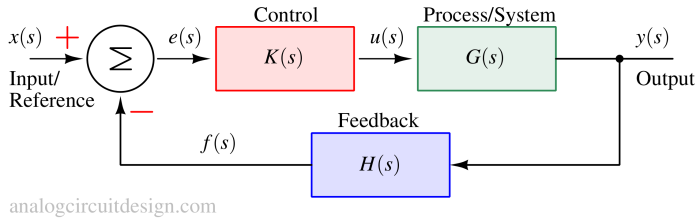
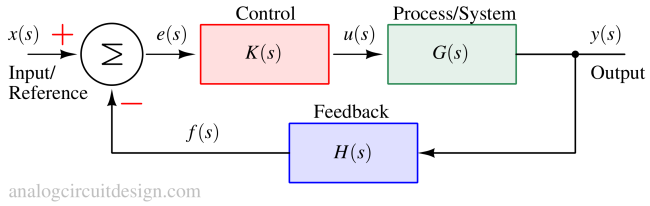
Feedback systems use a portion of the output signal to influence the input, improving stability, accuracy, and performance of electrical and control systems.
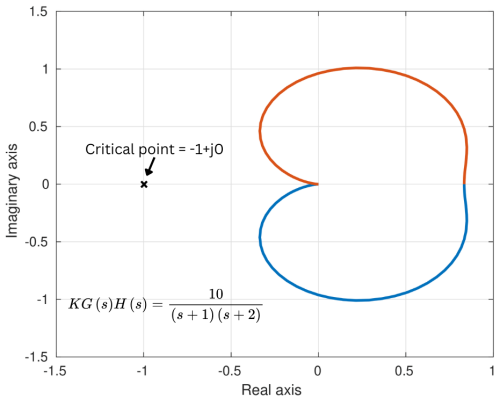
A Nyquist plot is a graphical representation of a system’s frequency response, showing the real and imaginary parts of the open-loop transfer function.
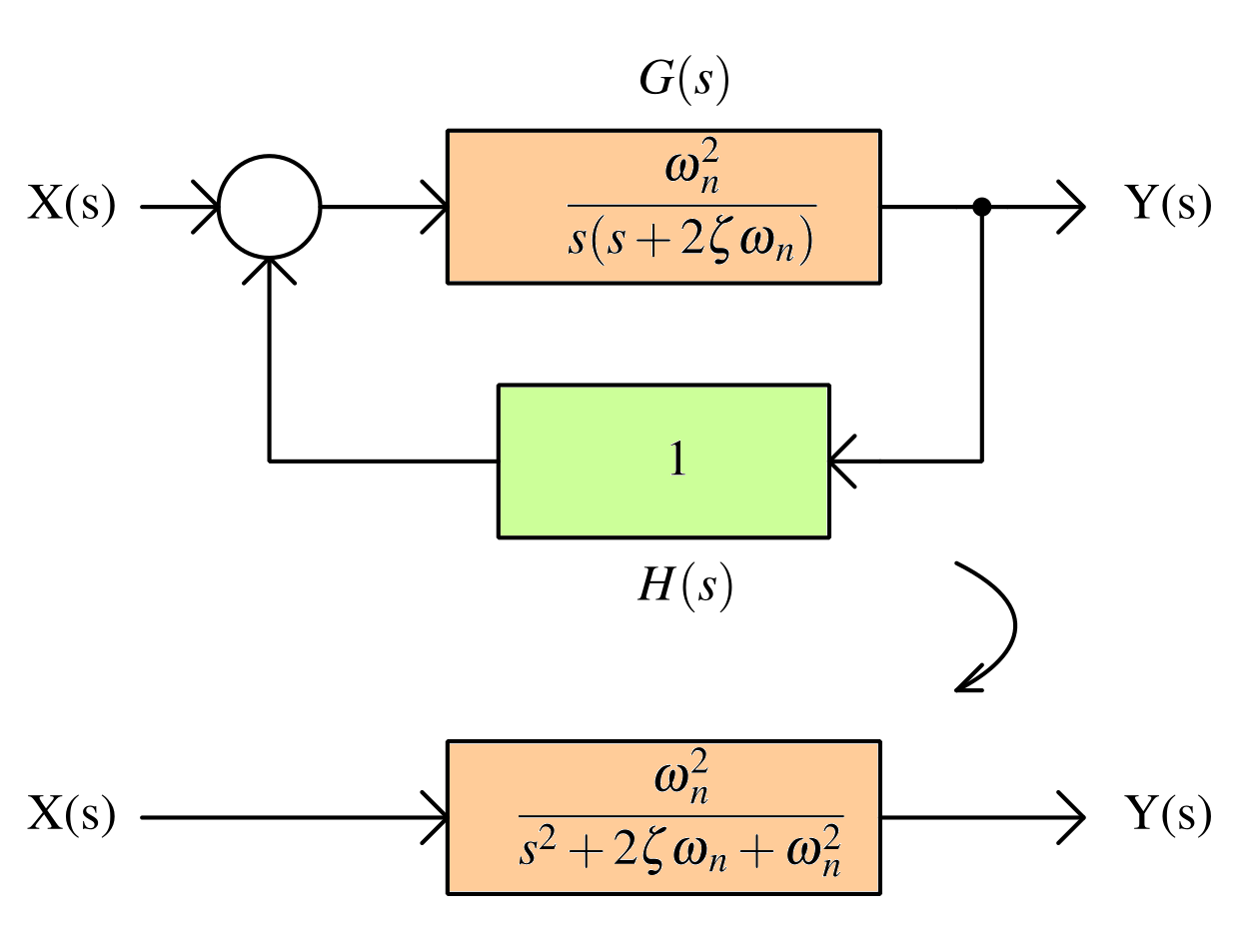
Second order systems are dynamic systems characterized by a second order differential equation, commonly seen in electrical systems.
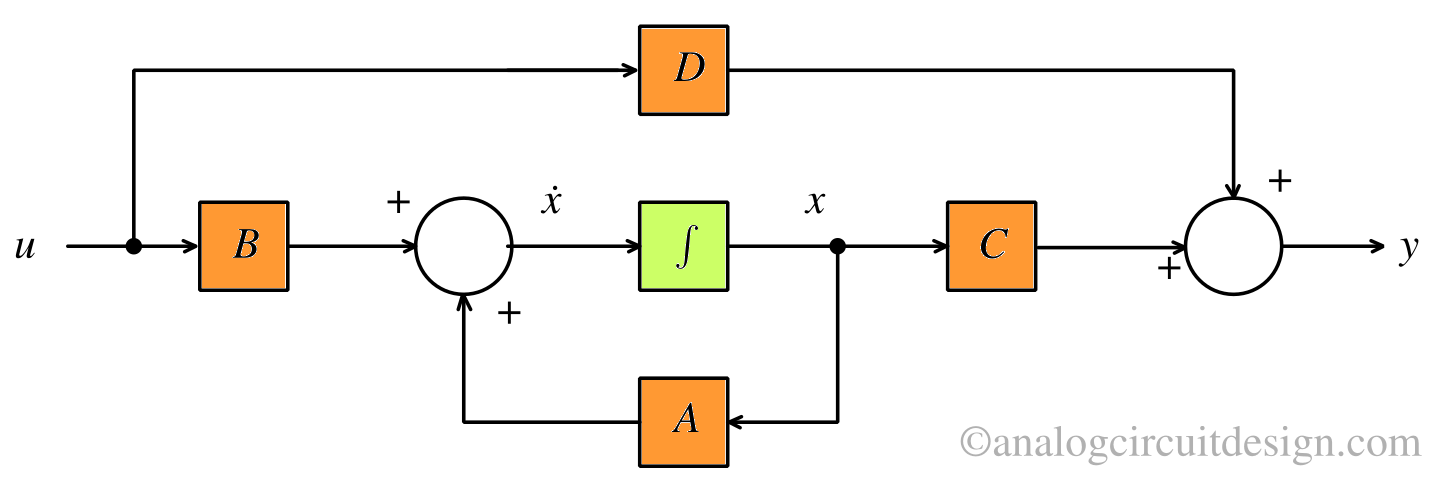
State space analysis models dynamic systems using a set of first-order differential equations representing system states, inputs, and outputs.
Root locus is a graphical method used to analyze how the roots of a feedback system’s characteristic equation change with varying system gain.
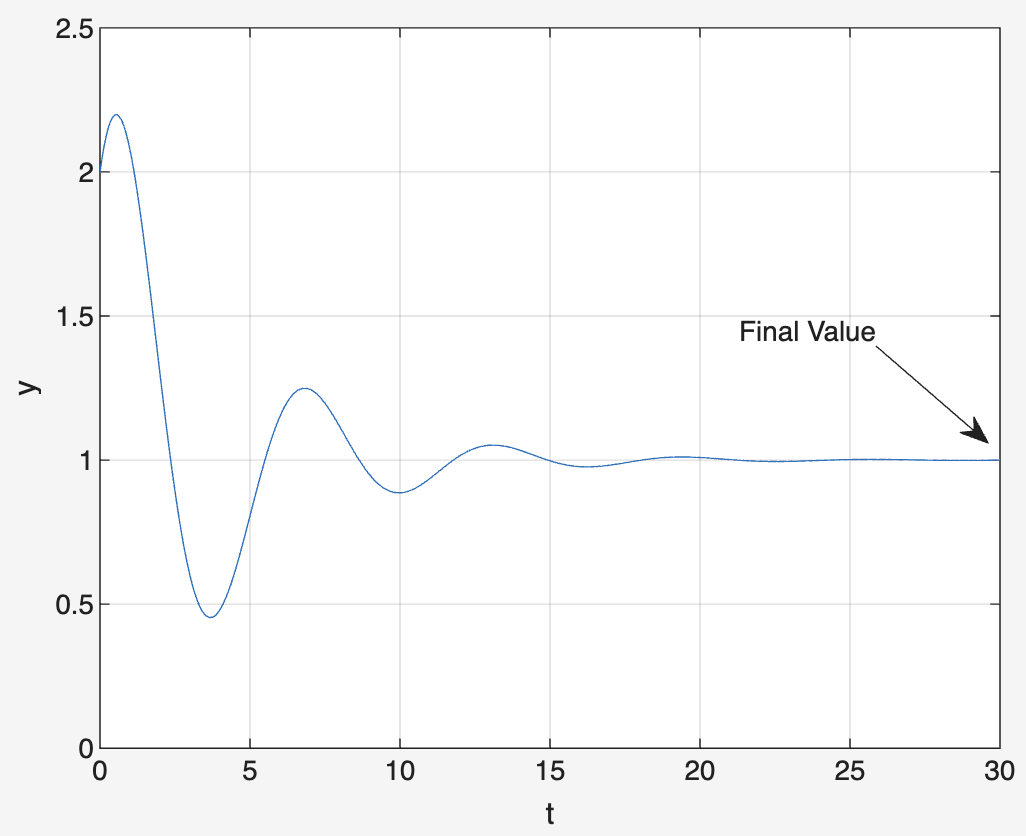
The final value theorem relates the steady-state value of a time-domain function to its Laplace transform, predicting long-term system behavior.
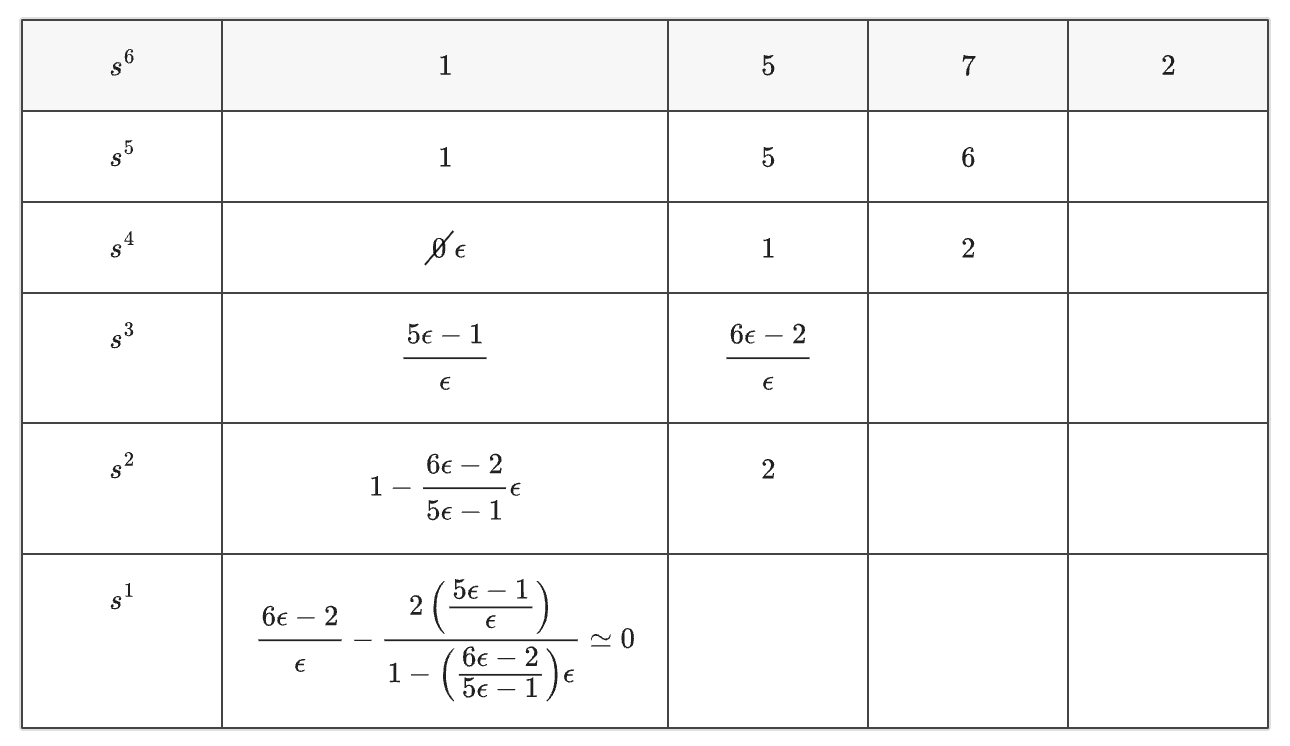
The Routh-Hurwitz criteria provide a systematic method to determine the stability of a linear control system by examining the signs and magnitudes of the coefficients of its characteristic equation.
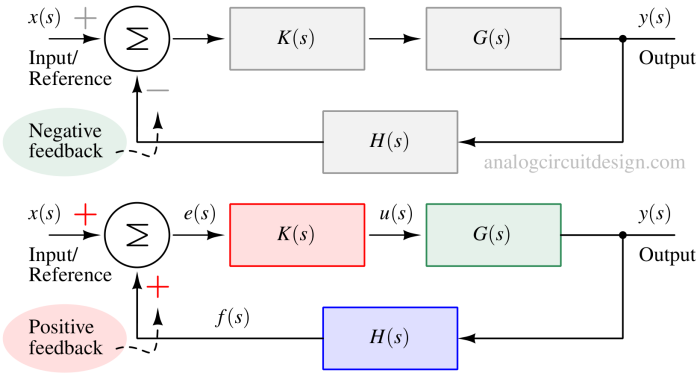
A Positive Feedback Circuit is one in which a portion of the output signal is fed back to the input in phase, reinforcing the input signal and increasing the overall gain.

Control systems manage, command, and regulate the behavior of other systems. They are broadly classified into open-loop and closed-loop types, used in automation and engineering applications.
Convolution is a mathematical operation that combines two signals to produce a third signal, representing how the shape of one is modified by the other.
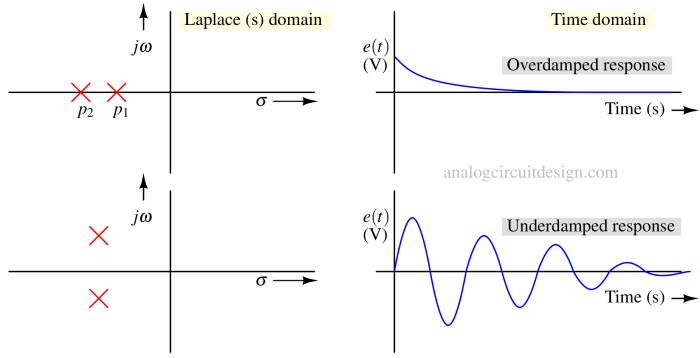
Stability in control systems refers to the ability of a system to return to its equilibrium state after a disturbance.
The Inverse Laplace transform converts a function from the s-domain back into the time domain, helping determine the actual time response of systems.
Phase margin and gain margin are measures of the stability of a control system, indicating how close the system is to oscillation.
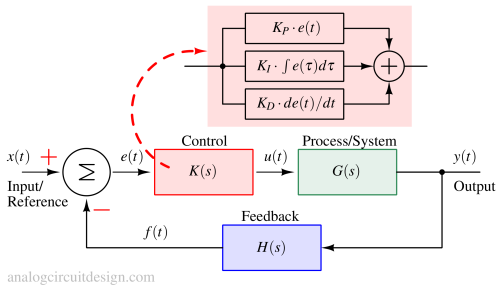
A Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller is a control system mechanism that continuously calculates error values and applies corrective action using proportional, integral, and derivative terms.
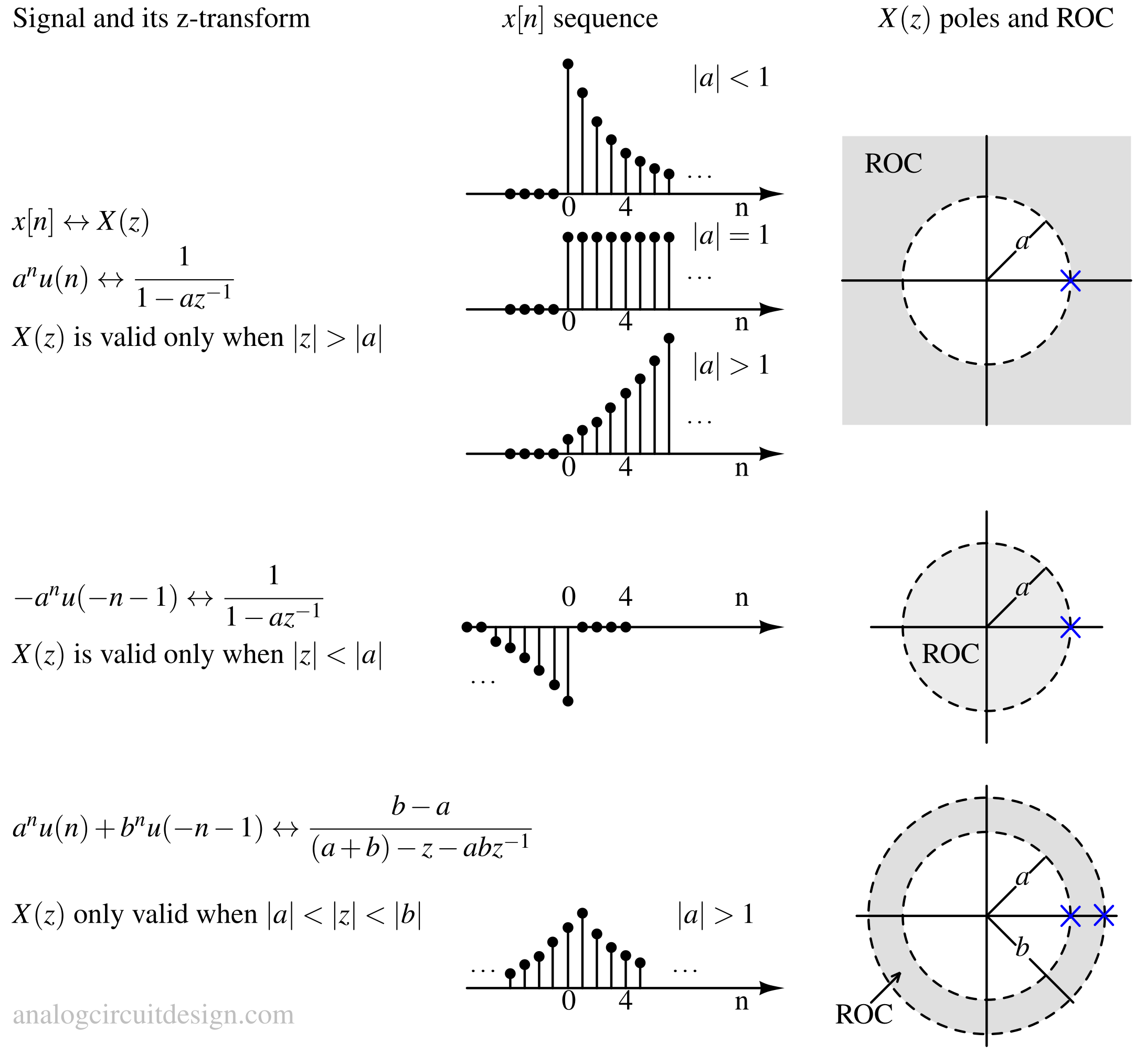
The Z-transform is a mathematical tool that converts discrete-time signals from the time domain into the complex frequency domain.
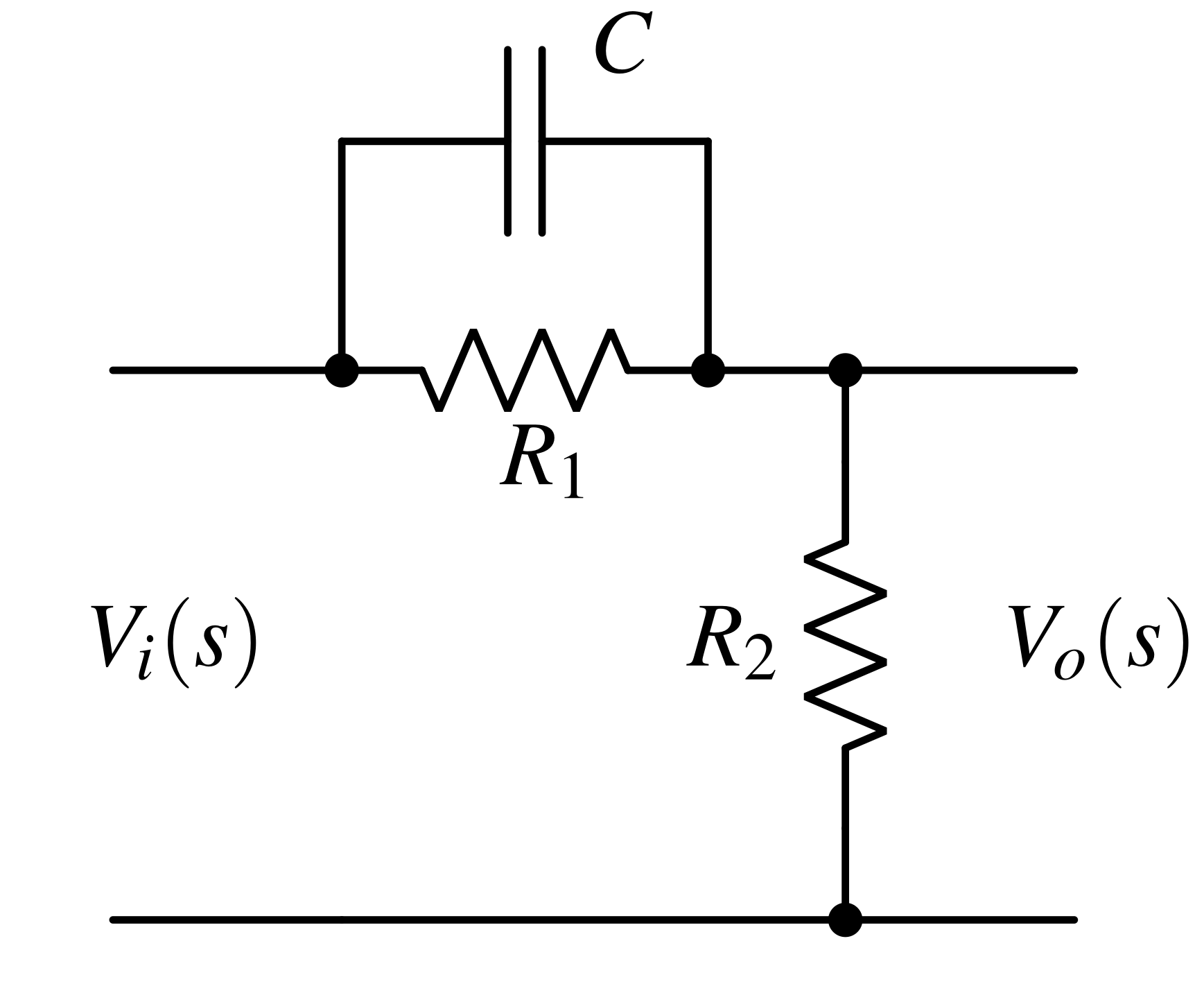
Lead and lag compensators are control system components used to improve system stability, transient response, and steady-state accuracy by adjusting phase and gain.
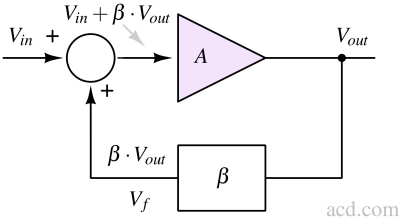
The Barkhausen criteria define the conditions for sustained oscillations in a feedback circuit-the loop gain must be unity and the phase shift must be zero or a multiple of 360.
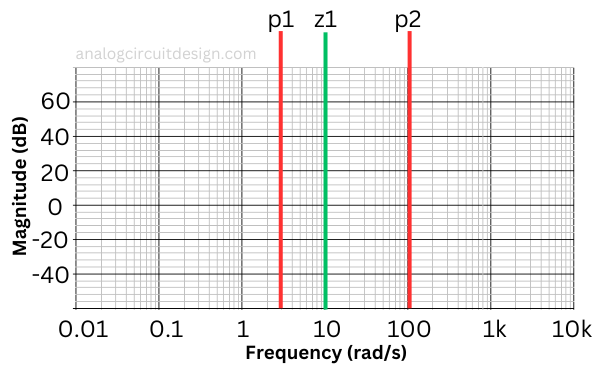
A Bode plot is a graph of a system’s frequency response, showing magnitude and phase versus frequency on logarithmic scales, commonly used in control systems and electronics.