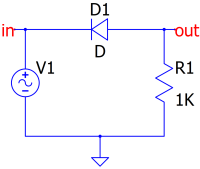
Diode¶
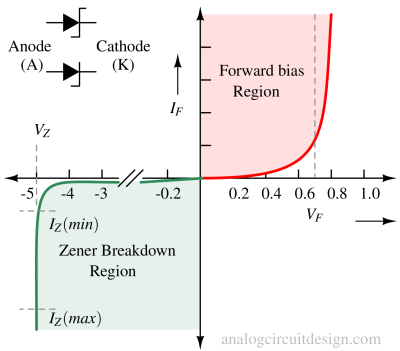
A Zener Diode is a special type of diode designed to operate in reverse breakdown region, maintaining a nearly constant voltage across it despite variations in current.

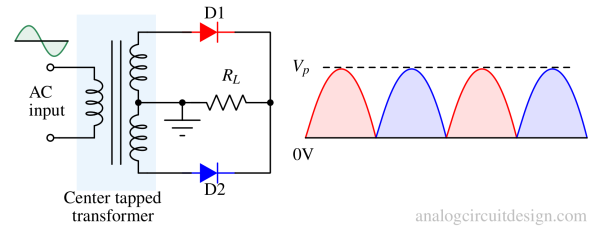
A half wave rectifier converts only one half of the AC input waveform into DC, using a single diode to allow current flow in one direction.
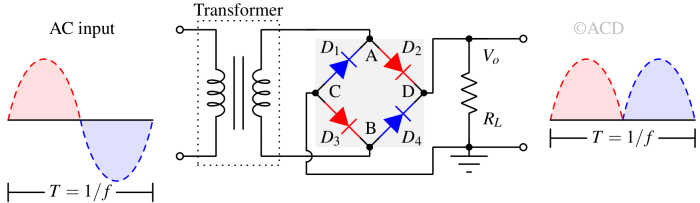
A bridge rectifier is an arrangement of four diodes that converts AC input into DC output by allowing current to flow in one direction during both halves of the input cycle.
Clipper circuits are used to limit the voltage level of a signal by removing portions of the waveform above or below a set threshold without distorting the remaining part.
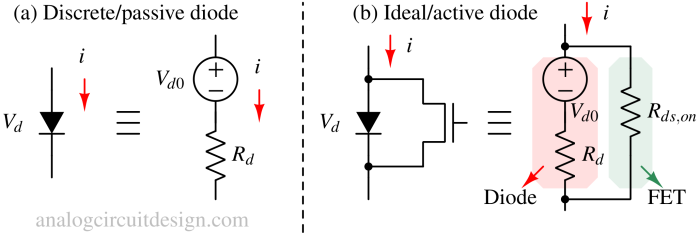
An active bridge rectifier uses MOSFETs instead of diodes to convert AC to DC with lower losses, improving efficiency in power supplies.
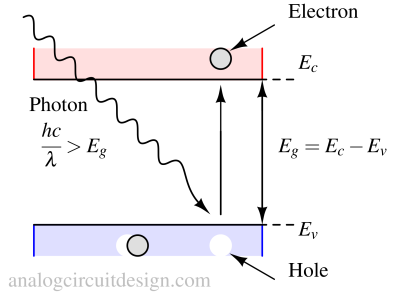
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that generates current when exposed to light, converting optical signals into electrical signals.
A light emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when a forward current passes through it.

Clipper circuits limit the voltage level of a signal without distorting the remaining part, while clamper circuits shift the signal’s voltage level by adding a DC bias.
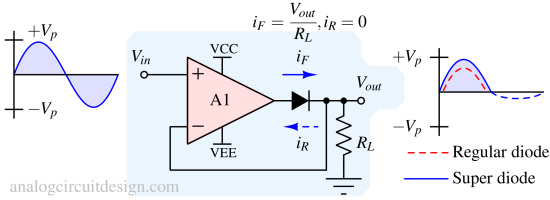
A super diode or precision rectifier is a diode paired with an operational amplifier to eliminate the forward voltage drop, allowing precise rectification of small signals.
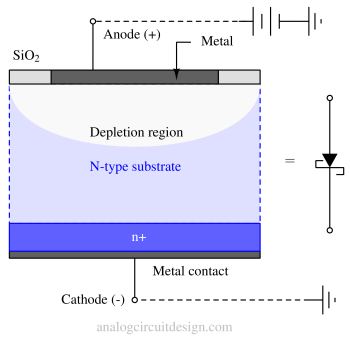
A Schottky diode is a semiconductor diode with a low forward voltage drop and fast switching capability.

A PN junction diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction.
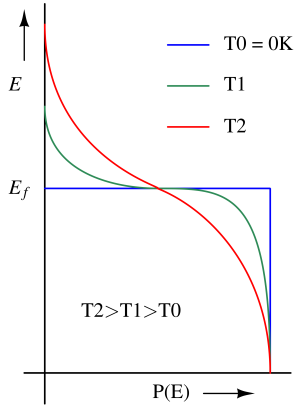
The Fermi energy level is the energy level at which the probability of finding an electron is 50% at absolute zero temperature.