Passives¶
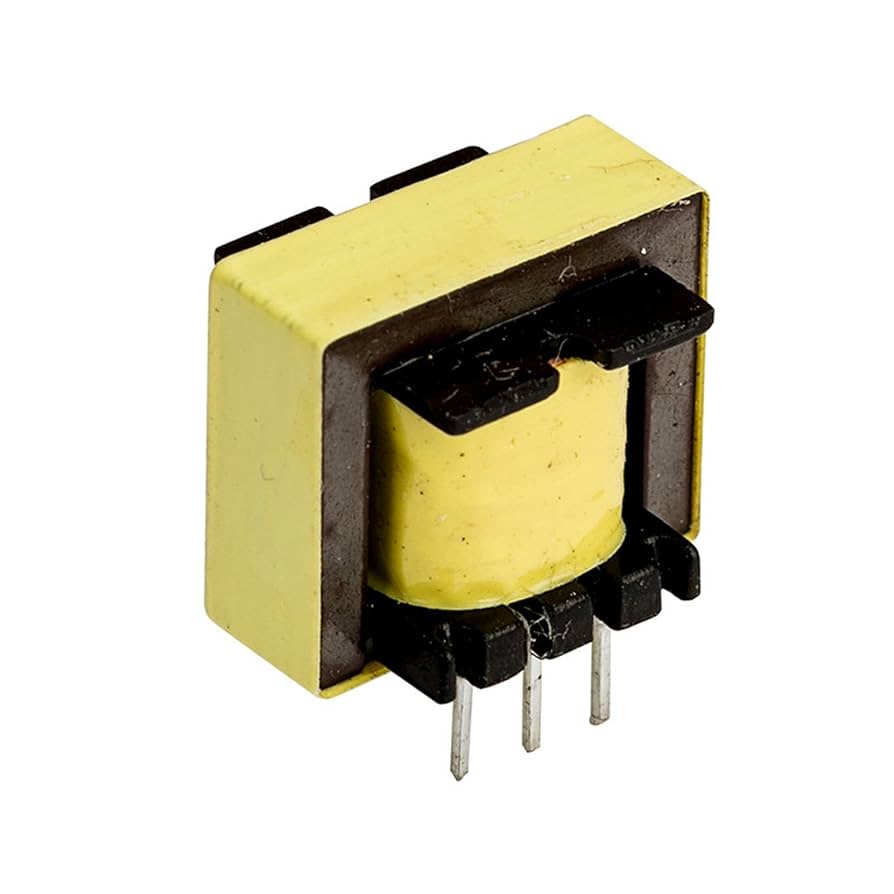
Audio transformers transfer audio signals between circuits while providing impedance matching, isolation, and noise reduction in sound systems.

An autotransformer is a type of transformer with a single winding that acts as both primary and secondary, providing voltage transformation with improved efficiency.
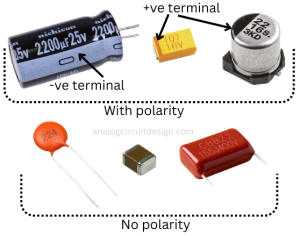
Capacitor specifications include capacitance value, voltage rating, tolerance, equivalent series resistance (ESR), and temperature coefficient, which determine performance in circuits.

Resistors are available in various types such as fixed, variable, thermistors, photoresistors, and precision resistors, each serving different purposes in circuits.
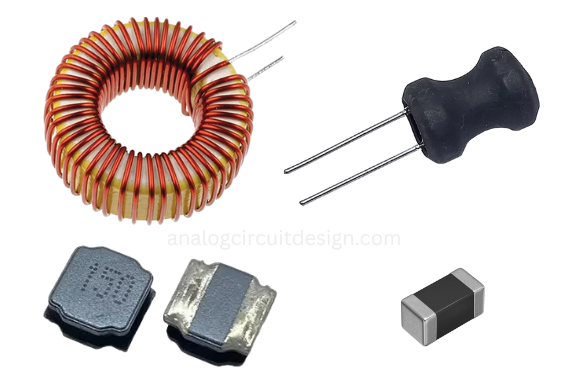
An inductor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in a magnetic field when current flows through it.
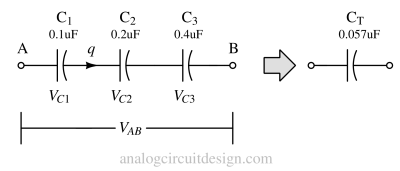
Capacitors in parallel combine to increase total capacitance, while capacitors in series result in a lower total capacitance than the smallest individual capacitor.
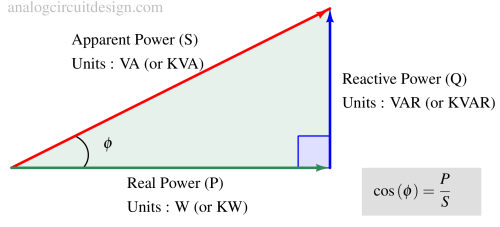
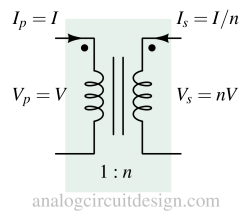
Transformers are rated in kVA instead of kW because their losses depend on voltage and current, not on the power factor of the load.

A supercapacitor is an energy storage device with very high capacitance, capable of storing and delivering large amounts of energy quickly.
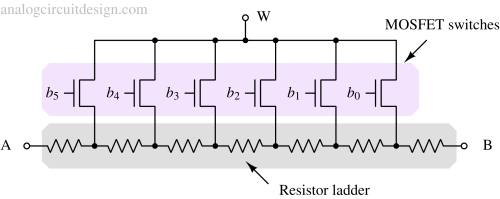
A digital potentiometer is an electronically controlled resistor that adjusts resistance in discrete steps using digital signals.
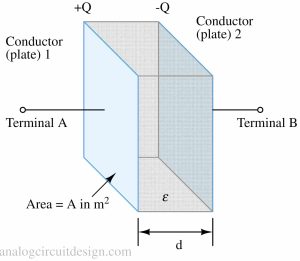
A capacitor is a passive electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field, consisting of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material.

Inductors in series add up to increase total inductance, while inductors in parallel result in a lower total inductance than the smallest individual inductor.
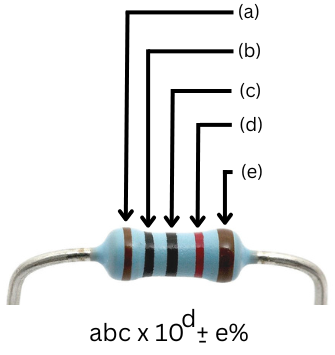
Resistor specifications include resistance value, tolerance, power rating, temperature coefficient, and material type, which determine their performance in circuits.

A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, changing voltage and current levels.
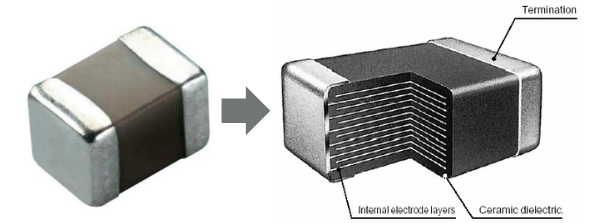
Capacitors come in various types, such as ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, film, and supercapacitors, each suited for specific applications.

Resistors in series add up to increase total resistance, while resistors in parallel result in a lower total resistance than the smallest individual resistor.
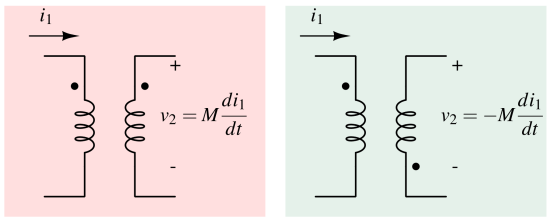
Dot notation indicates the relative polarity of transformer windings, showing which ends have the same instantaneous voltage phase.
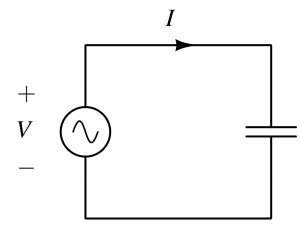
In AC circuits, capacitors store and release energy by charging and discharging with the alternating voltage, causing a phase shift between voltage and current.
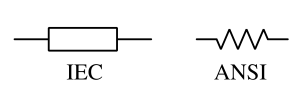
A resistor is a passive electronic component that limits current flow and drops voltage in an electrical circuit.
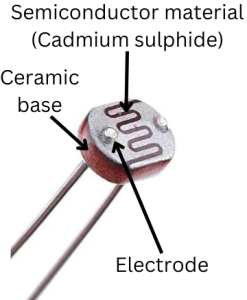
A light dependent resistor (LDR) is a photoresistive device whose resistance decreases with increasing light intensity.
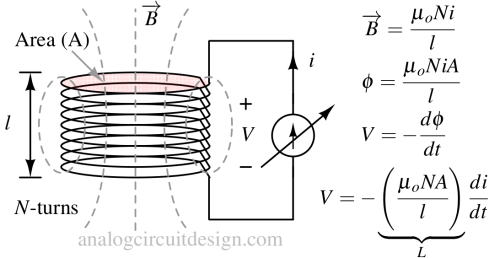
Self-inductance is the property of a coil to oppose changes in its own current, while mutual inductance is the ability of one coil to induce voltage in another nearby coil.