Diac¶
A DIAC is a 2-terminal device which turns-on only after voltage across its 2-terminals is higher than its breakdown voltage (VBO). DIACs are used in the triggering of Triacs.
A Diac is a full-wave (bi-directional) semiconductor switch without any extra control (Gate) terminal. It can be turned on in both the polarities. The Breakdown voltage (VBO) is symmetric in both the directions.
Advantages and disadvantages of Diac¶
The main advantage of using this device is :
- It acts as a simple comparator-switch. If the voltage is below VBO, Diac behaves as a open switch. If the voltage across the Diac increases above VBO, Diac turns on as a closed switch and remains closed till the current is higher than the holding current.
- The I-V characteristics is symmetric, so the operation and circuit design is simple.
- When Diac is used to trigger Triac, the trigger characteristics become more symmetric.
The main disadvantage of Triac :
- Though it is a symmetric device, it does not offer phase control because it does not have a gate terminal.
Current voltage characteristics of a Diac¶
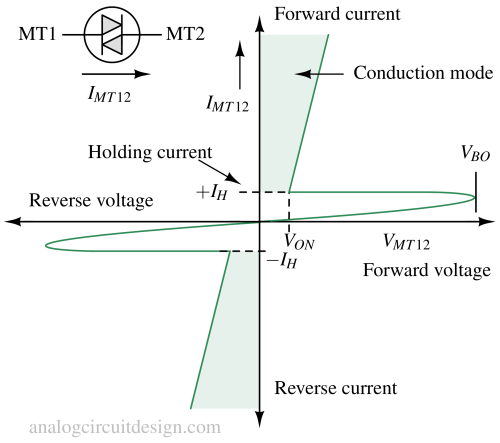
The behavior resembles 2-SCRs in inverse parallel with the gate terminal open. When the current is less than VBO, the current is very less. This current is mainly the drift current. The voltage is not enough to trigger an avalanche breakdown. When the voltage is higher than VBO, the avalanche breakdown happens. The current is extremely high if the Diac is held with a voltage source at VBO. This high current can damage the Diac permanently. In practical applications, Diac is always operated with a series current limiting resistor.
Holding current is the minimum current that keeps the Diac in conduction mode. If the current is less than the holding current (IH) then the voltage becomes higher than VON.
Construction and Symbol¶
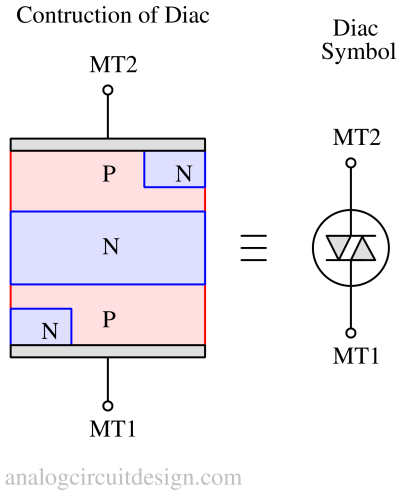
It is a device which consists of four layers and two terminals. The construction is almost the same as that of a triac. However there are some notable and important differences:
- There is no gate control terminal in a Diac.
- Diac is symmetric device by construction as well as doping.
- The current-voltage relationship is symmetric in Diac while for Triac the current-voltage is not symmetric.
Application of Diac¶
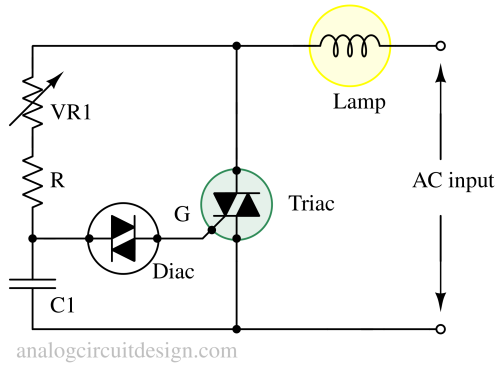
A DIAC is mainly used to trigger a TRIAC circuit because of the simplicity it offers. There is no need of threshold comparision and a discharge transistor when a Diac is used. The Diac is connected to the gate terminal of the TRIAC. As shown in the figure, when the capacitor is charge till VBO, the Diac turns on and triggers the Triac. The trigger gate current of Triac is provided by the discharge current of capacitor. The voltage rating of the capacitor should be greater than Diac trigger voltage (VBO).
Some other applications of a DIAC (along with a Triac) :
- Lamp dimmer circuit.
- Heat control circuit.
- Speed control of a AC motor.