Flex sensor¶
A flex sensor is a kind of sensor that is used to measure the amount of bending. It changes its resistance based on how much bending or flexing it undergoes. It's essentially a bendable resistor that can detect the degree of bending and convert it into an electrical signal.
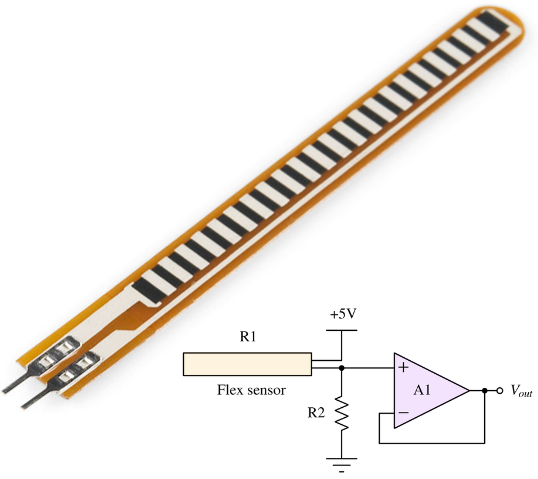
Properties of a flex sensor¶
Types of flex sensor¶
These sensors are classified into two types based on their size, namely 2.2-inch flex sensor & 4.5-inch flex sensor. The working principle is identical.
Pin configurations¶
It is a two-terminal device. The terminal names are called P1 and P2. It has no polarized terminal such as a diode, which means there is no positive & negative terminal.
Working principle¶
Flex sensors are typically made of a flexible substrate, such as polyester, with conductive material (usually carbon) applied to its surface. As the sensor bends, the separation between the conductive particles increases, increasing resistance. When the sensor is at rest or in a neutral position, its resistance remains relatively constant (~ 25kΩ). However, when the sensor is bent, its resistance changes. The degree of change in resistance depends on the design and materials of the sensor.
Output of the flex sensor¶
Flex sensors provide analog output. This means that the resistance change is proportional to the degree of bending. The electrical signal can be connected to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to convert it into a digital value that a microcontroller or a computer can process.
Calibration¶
Flex sensors often require calibration to convert the resistance change into meaningful units, such as degrees of bending. This involves mapping the sensor's resistance values to the corresponding bending angles. Different flex sensors might have varying sensitivity, range, and linearity characteristics. It's important to choose a sensor that suits your specific application requirements.
Integration¶
Flex sensors can be integrated into circuits using soldering or conductive adhesives. They can be interfaced with microcontrollers, Arduinos, Raspberry Pi boards, or other electronic devices to process and analyze the sensor data.
Limitations¶
Flex sensors might experience wear and tear over time, especially with repeated bending. Additionally, they can be influenced by factors like temperature and humidity, which could affect their accuracy.
Applications of flex sensors¶
Flex sensors find applications in various fields, including robotics, wearables, medical devices, gaming peripherals, and industrial applications. For example, they can be used in gloves to measure finger movements or in exoskeletons to detect the user's motion.
Specifications of a common flex sensor¶
The specifications and features of this sensor include the following.
- The operating voltage of this sensor ranges from 0V to 5V
- The power rating: 1W (peak) and 0.5W (Continous)
- Operating temperature range: -45ºC to +80ºC
- Flat/Neutral position resistance: 25KΩ
- Tolerance: ±30%
- The range of bend resistance will range from 40KΩ-130KΩ