Schottky diode¶
It is a metal-semiconductor junction (instead of a regular semiconductor-semiconductor junction) that offers a very low forward voltage drop (0.2 to 0.4V) and a very fast switching action (very fast reverse recovery time).
Similar to a regular PN junction diode, a Schottky diode also conducts when forward-biased and becomes an open circuit if reverse-biased. However, a regular PN junction diode has a typical forward voltage drop of 0.65-0.75V, while a Schottky diode has a forward voltage drop of 0.2-0.4V.
Suppose a regular diode carries 1A of current and has 0.7V of forward voltage drop. It means the power dissipation through it is 0.7W. If a Schottky diode is used instead, the power wasted could be 0.4W, which is 43% lesser than a regular diode.
Construction of a Schottky diode¶
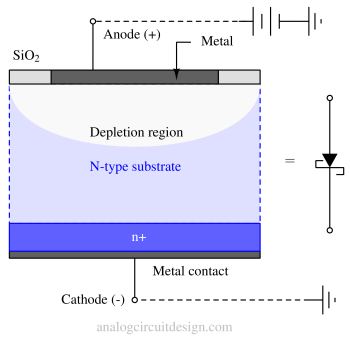
Schottky diode consists of the following layers:
- Metal contact (Anode)
- Lightly doped N-region. Also called the epitaxial layer. This region along with the metal-semiconductor junction decides I-V characteristics.
- Heavily doped N-region.
- Metal contact (Cathode)
Generally, n-type silicon and n-type GaAs are used in commercially available Schottky diodes.
Current-voltage relationship of Schottky diode¶
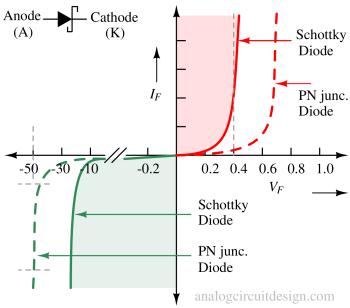
The I-V characteristics of a Schottky diode look similar to a PN junction diode. However, the forward voltage (knee voltage) is lesser than the PN junction. Also, the magnitude of reverse breakdown voltage is lower for the Schottky diode.
Richardson constant in Schottky diode¶
The current-voltage relationship of the Schottky diode is similar to the PN junction diode. The primary difference is between the reverse bias current IS. There is an additional Richardson constant A* in the Schottky diode.
$$I_D=I_S\left[\exp{\left(\cfrac{V_D}{\eta{}kT/q}\right)}-1\right]$$
$$I_S=AA^*T^2\exp{\left(\cfrac{-qphi{}_B}{kT}\right)}$$
(phi{}_B) is barrier height, A is junction area, A* is Richardson constant, and T is temperature.
Advantages and disadvantages of Schottky diode¶
There are several advantages and disadvantages of Schottky diodes as listed below:
Advantages¶
- Due to the absence of a storage charge, its reverse recovery is faster than a regular diode.
- Low forward voltage drop.
- Low Junction capacitance.
Disadvantages¶
- Higher leakage current. It increases with an increase in temperature.
- The reverse breakdown voltage is lower than a regular PN junction diode.
Applications of Schottky diode¶
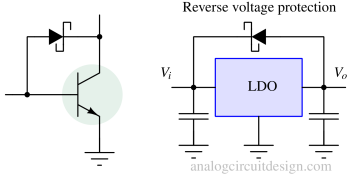
- Voltage clamping. Commonly used to prevent BJT from going into saturation region.
- Reverse current and discharge protection. Usually, LDOs having large capacitors at the output are protected from reverse voltage using a Schottky diode.
- Switch mode power supplies
- RF-mixer and detector diode.