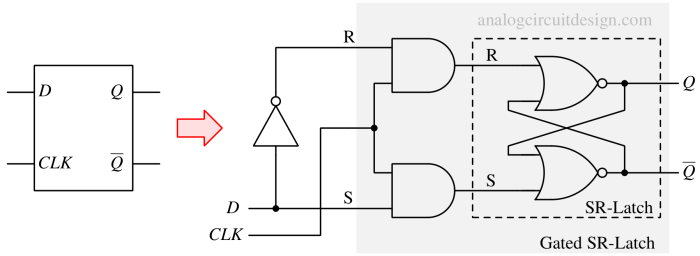
Digital¶

An SR latch stores a binary state based on Set and Reset inputs, while an SR flip-flop adds clock control for synchronized data storage.
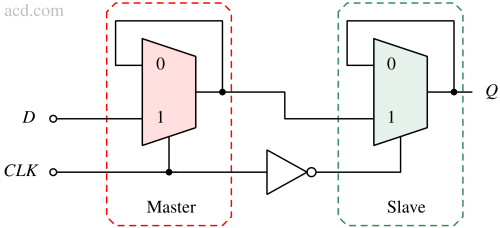
Latches store data while the enable signal is active, whereas flip-flops capture and store data on a clock edge, providing synchronized memory in digital circuits.
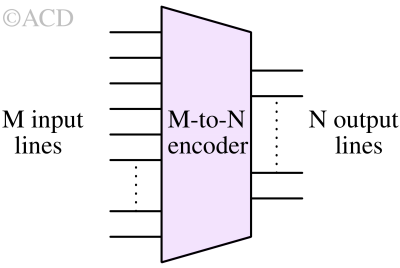
A digital encoder converts multiple input lines into a smaller number of output lines, representing the input as a binary code.
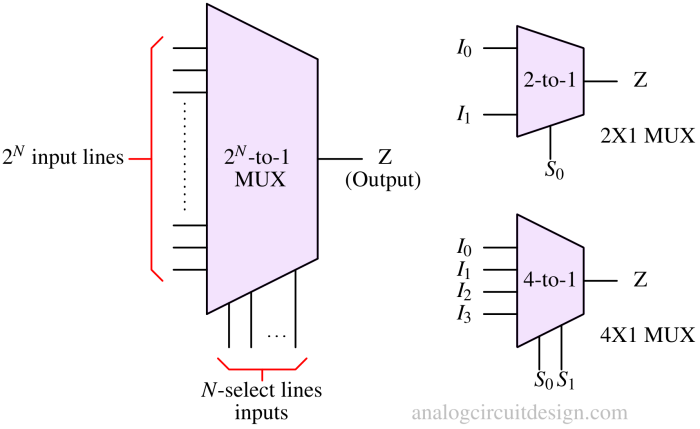
A multiplexer selects one of several input signals and forwards it to a single output line based on select signals.
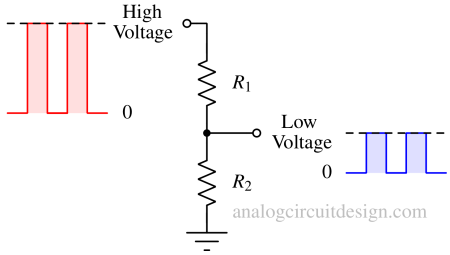
A level shifter circuit converts voltage levels from one logic family or signal domain to another, enabling proper interfacing between devices.
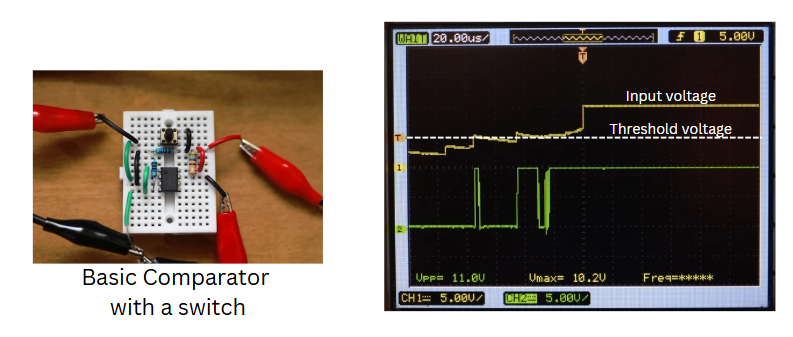
A Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis that converts a noisy or analog input signal into a clean digital output.
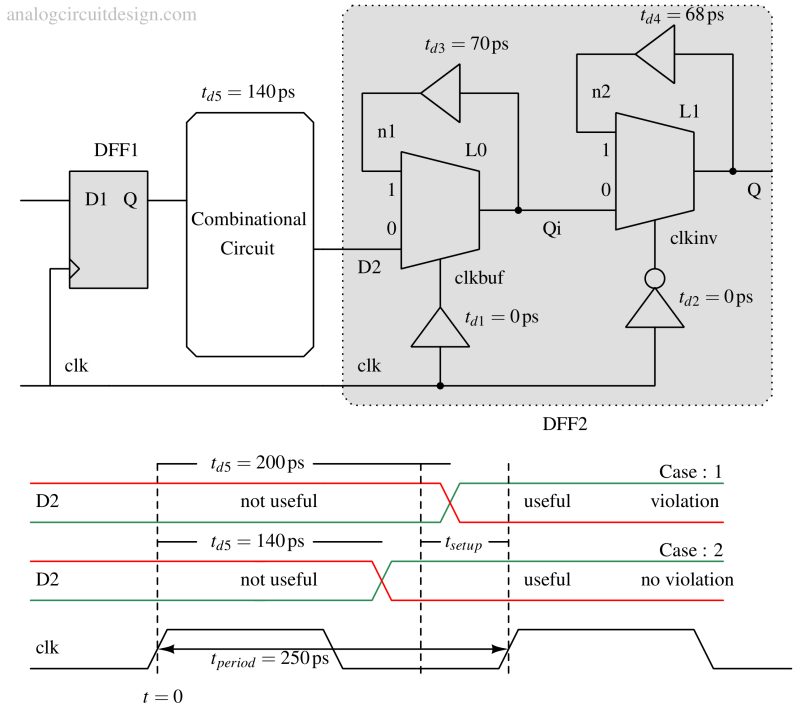
Setup time is the minimum period before a clock edge that data must be stable, while hold time is the minimum period after the clock edge that data must remain stable.

A demultiplexer is a digital circuit that takes a single input and routes it to one of several output lines based on select signals.
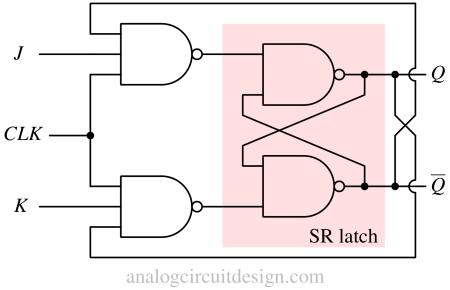
JK latches and flip-flops store binary information, with the JK flip-flop providing edge-triggered control to avoid indeterminate states.
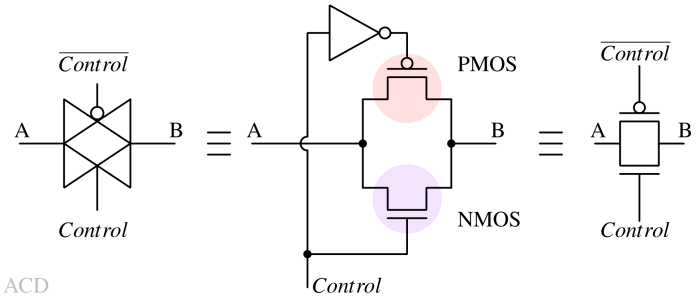
A transmission gate is a bidirectional switch that uses parallel NMOS and PMOS transistors to pass or block signals controlled by a gate voltage.
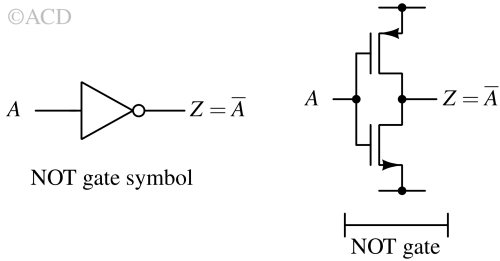
Basic logic gates are the building blocks of digital circuits. Common types include AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR, each performing a unique logic function.