Oscillators¶
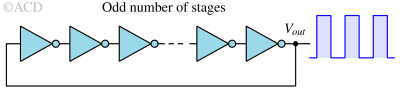
A ring oscillator generates periodic oscillations by connecting an odd number of inverters in a loop, producing a continuous square wave output.
Electronic oscillators generate periodic waveforms such as sine, square, or triangle signals without an external input signal.
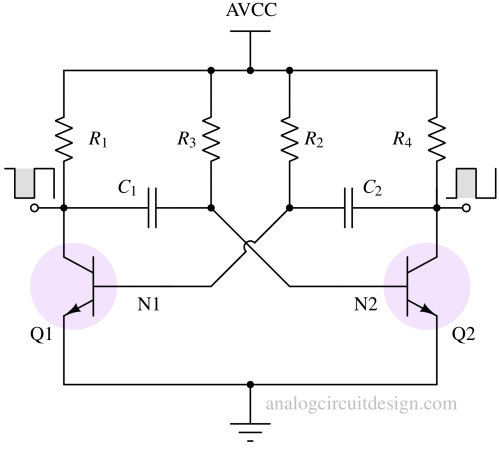
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, or pulse waveforms and can operate in astable, monostable, or bistable modes.
The 555 timer IC is one of the most versatile chips in electronics, used for generating delays, pulses, and oscillations. Its simple design and wide applications make it a must-know component for hobbyists and engineers alike.
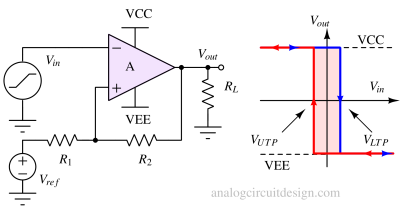
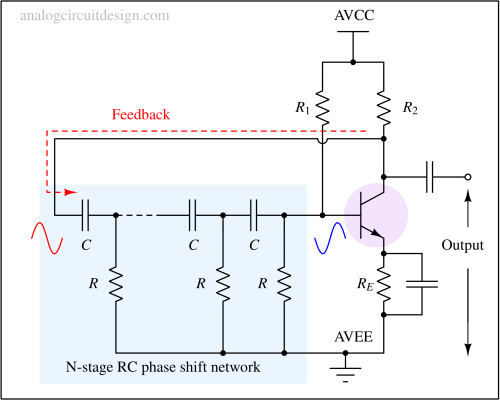
An RC relaxation oscillator generates a periodic waveform, such as a square or triangular wave, using a resistor-capacitor network and a switching device.
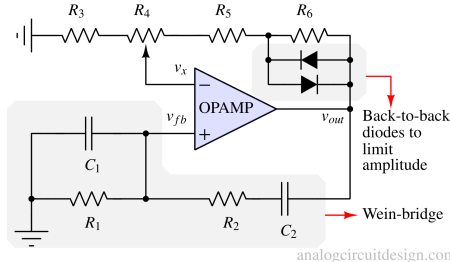
A Wien bridge harmonic oscillator generates sinusoidal waveforms using a bridge circuit composed of resistors and capacitors along with an amplifier.
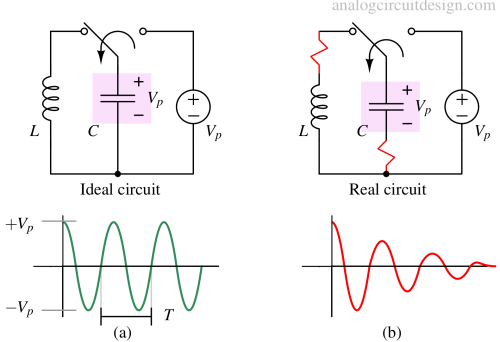
LC oscillators generate sinusoidal waveforms using an inductor (L) and capacitor (C) to determine the oscillation frequency.
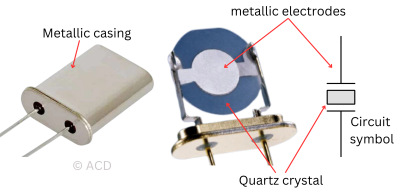
A quartz crystal oscillator uses the mechanical resonance of a quartz crystal to generate a precise and stable frequency output.
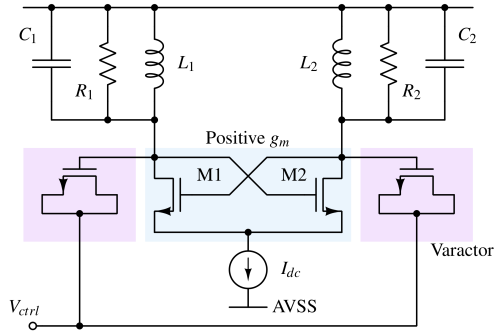
A Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) is an electronic circuit that generates a periodic waveform whose output frequency varies in response to an applied control voltage.

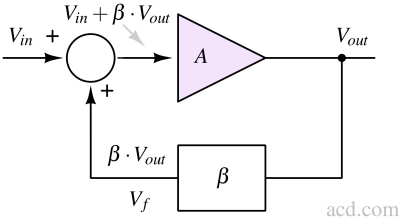
The Barkhausen criteria define the conditions for sustained oscillations in a feedback circuit-the loop gain must be unity and the phase shift must be zero or a multiple of 360.