Power¶
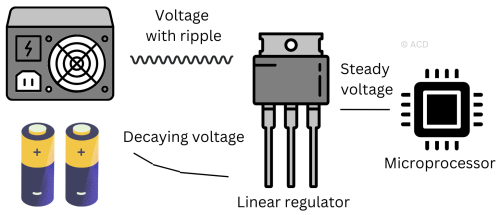
Linear and low dropout regulators (LDOs) provide a stable output voltage from a higher input voltage, with LDOs operating efficiently even with a small input-to-output voltage difference.
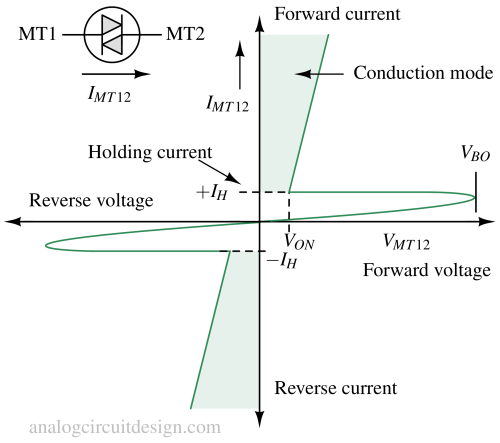
A DIAC is a bidirectional semiconductor device that conducts current only after its breakover voltage is exceeded, commonly used for triggering TRIACs.
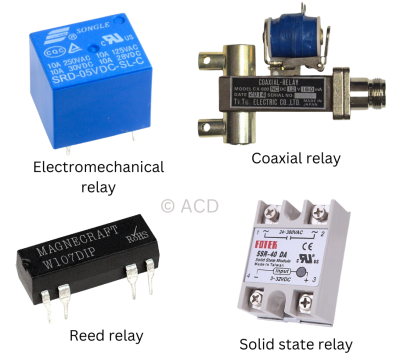
A relay is an electrically operated switch that uses an electromagnet to open or close contacts, controlling a high-power circuit with a low-power signal.
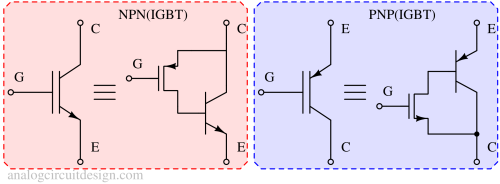
An IGBT is a semiconductor device that combines the high input impedance of a MOSFET with the low conduction loss of a bipolar transistor, used for switching and amplification.
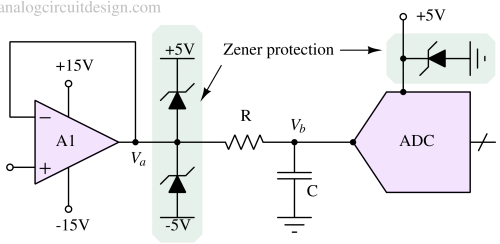
Input protection clamps safeguard electronic circuits by limiting voltage spikes and preventing excessive voltage from damaging sensitive components.

Power factor measures the efficiency of electrical power usage, while power factor correction improves it by reducing reactive power in AC circuits.
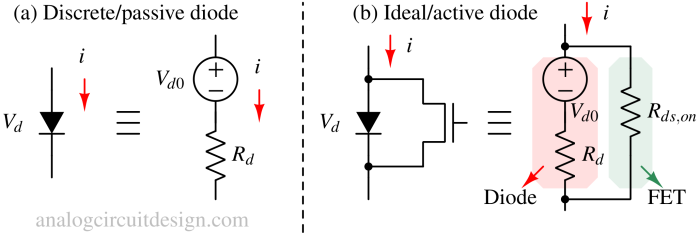
An active bridge rectifier uses MOSFETs instead of diodes to convert AC to DC with lower losses, improving efficiency in power supplies.
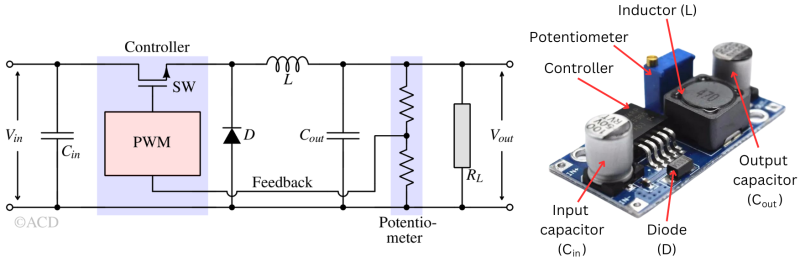
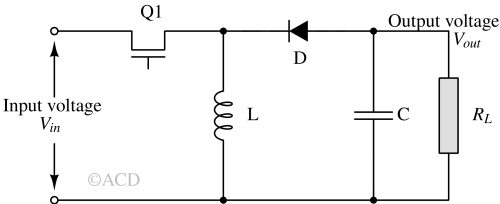
A buck converter is a DC-DC power converter that steps down the input voltage to a lower output voltage using a switch, inductor, diode, and capacitor.
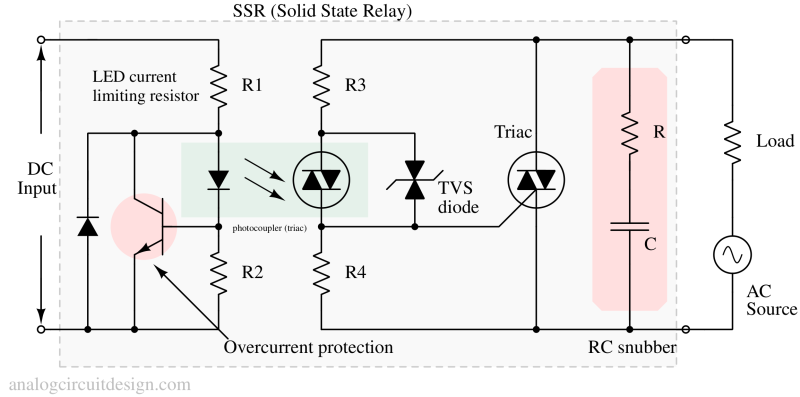
A solid state relay (SSR) is an electronic switching device that switches AC or DC loads without moving parts, using semiconductor components.
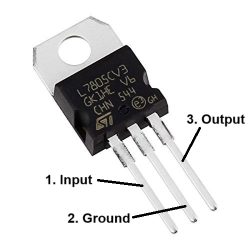
The LM7805 is a fixed 5V linear voltage regulator that provides a stable output voltage with built-in thermal and short-circuit protection.

The LM317 is an adjustable voltage regulator that provides a stable output voltage ranging from 1.25V to 37V by using external resistors.
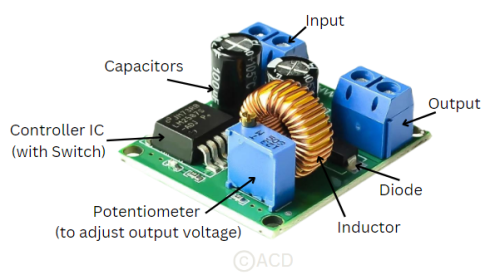
A boost converter is a DC-DC power converter that steps up the input voltage to a higher output voltage using an inductor, switch, diode, and capacitor.
A buck-boost converter is a DC-DC power converter that can step up or step down the input voltage to produce a regulated output voltage.
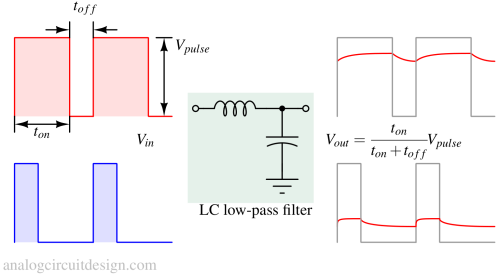
A switch mode power supply converts electrical power efficiently using high-frequency switching and energy storage components like inductors and capacitors.
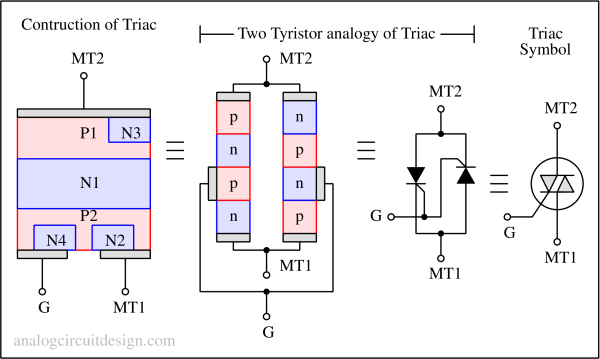
A TRIAC is a bidirectional semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered, used for AC power control.