Ideal and real sources¶
Ideal sources are theoretical energy models used to simplify analysis. Both ideal voltage and current sources do not capture some real world phenomena. E.g., why with output loading, voltage drops in a voltage source ? To explain these we have to consider output resistance associated with real sources.
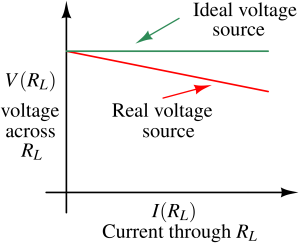
Ideal vs Real voltage source¶
An ideal voltage source will maintain the desired voltage across its terminal irrespective of the magnitude and direction of the current being drawn from it.
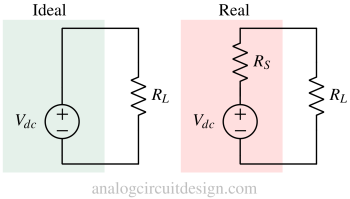
An actual voltage source's output voltage drops when more current is drawn (as shown in the following figure). It is modeled as an ideal voltage source with series resistance. The voltage drop happens because of drop (also called IR drop) across the RS (called source impedance/resistance). So, the effective voltage across the load resistance drops, which is undesirable. Therefore a voltage source having less source resistance is desired.
In case of ideal voltage source, the voltage appearing across RL is :
$$V_{RL}=V_{dc}$$
In case of real voltage source, the voltage appearing across RL is :
$$V_{RL}=\cfrac{R_L}{R_S+R_L}V_{dc}$$
With increase in source resistance RS, we see that VRL drops.
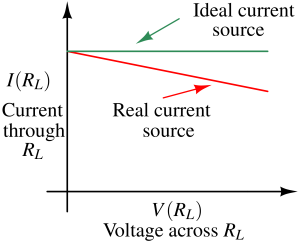
Ideal vs Real current source¶
An ideal current source will push/pull the desired current across its two terminals irrespective of the magnitude and direction of the voltage.
An actual current source's output current changes depending on the output voltage. Usually, it is modeled as an ideal current source with a large parallel resistance (called output impedance/resistance). As the voltage increase, the parallel resistance (RP) steals some current due to which there is lesser current available for RL.
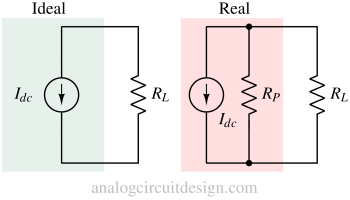
In case of ideal current source, the current through RL is :
$$I_{RL}=I_{dc}$$
In case of real current source, the current through RL is :
$$I_{RL}=\cfrac{R_P}{R_P+R_L}I_{dc}$$
With increase in output resistance RP, we see that IRL increases. With infinite RP, entire current flows through RL.