LM35 - Temperature sensor¶
LM35 is a temperature-measuring device with an analog output voltage proportional to the temperature. It provides output voltage in the Celsius with only a single point calibration. The sensitivity of LM35 is 10 mV/°C. As temperature increases, the output voltage also increases, e.g. 400 mV means 40°C. It is a 3-terminal sensor that ambient temperatures ranging from -55°C to 150°C. LM35 gives temperature output that is more well-controlled than thermistor output.
LM35 Pinouts¶
| Pin No. | Pin Name | Funtionality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power pin (4 to 20V) |
| 2 | VOUT | 0mV + 10mV/C analog output |
| 3 | GND | Connected to 0V |
Specifications of LM35 temperature sensor¶
- Operating Voltage: 4 V to 30 V
- Sensor gain: 10mV/°C
- Linearity Error / Accuracy: ±1/4°C (for 0°C to +100°C)
- Operating Temperature: -55°C to +150°C
- Output Impedance: 0.1 Ω for 1mA load
- Quiescent Current: 60 μA (typical)
- Package Type: TO-92, TO-220, SOIC
- Output Type: Analog
Alternatives to LM35 temperature sensor¶
- TMP36
- DHT11
- DS18B20
- LM34
- RTD PT100
Application circuit diagram of LM35 temperature sensor¶
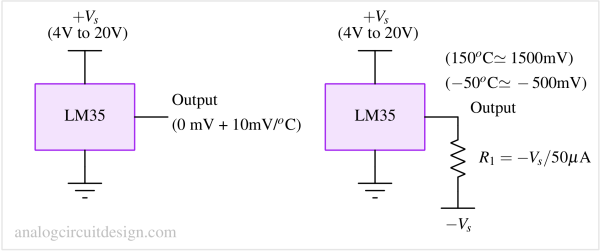
Applications of LM35 temperature sensor¶
- Thermal safety for automotive systems.
- It can be used in HVAC applications as a temperature measurement device.
- It can be used for battery temperature measurement. It can detect battery overheating.
Difference between Thermistors and LM35 temperature sensor¶
| Parameter | Thermistors | LM35 |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance tolerance | Large : Not well controlled | Small : +-1.5% tolerance across temperature. Well controlled |
| Sensitivity | Inconsistent : Very large at low temperature and very low at high temperature | Consistent : Uniform across temperature |
| Calibration point | Multiple calibration point because of nonlinearity across wide range | Only one point calibration is need because of linearity |
| Self heating | Increased power consumption with temperature. | Decreased power consumption with temperature |
| Sensor drift | Large sensor drift | Small sensor drift |
| Cost | Sensor cost maybe low but additional circuitry is required for operation across wide range | Sensor cost high but does not require additional circuits |