Norton's Theorem¶
Norton's theorem states, "Any linear electrical network containing only voltage sources, current sources, and resistances can be replaced by a single constant current source (Inorton) in parallel with a single resistor (Rnorton)."
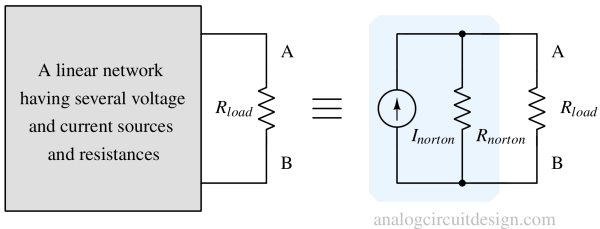
Using Norton theorem to simplify circuits¶
Norton's theorem is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that simplifies complex linear circuits to a simpler equivalent circuit. An example to simplify circuits is shown below using a well-defined procedure:
Identify the load and the network¶
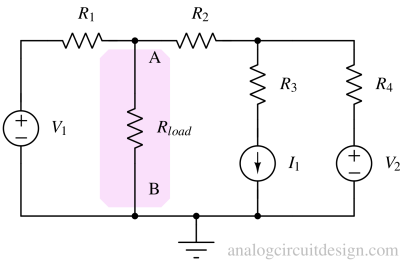
Find the short circuit current by shorting nodes A and B¶
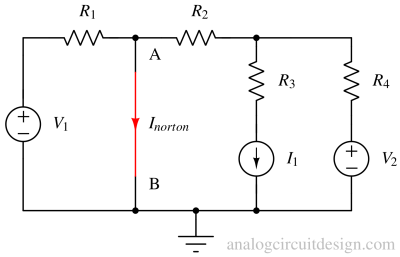
Using the superposition theorem,
$$I_{norton}=\cfrac{V_1}{R_1}+I_1\cfrac{R_4}{R_2+R_4}+\cfrac{V_2}{R_2+R_4}$$
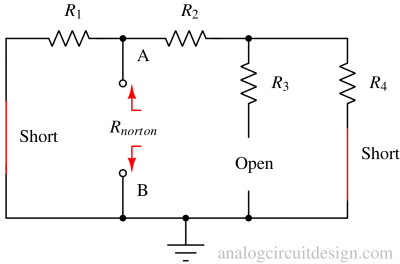
Find the equivalent resistance¶
The equivalent Rnorton is the resistance the circuit between terminals A and B would have if a short circuit replaced all ideal voltage sources and an open circuit replaced all ideal current sources.
$$R_{norton}=R_1||(R_2+R_4)$$
The method of finding the resistance is identical to Thevenin resistance.
Create the Norton network¶
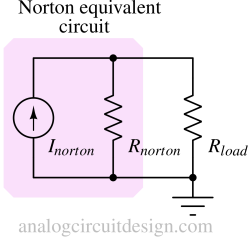
Step 5: Find the voltage across the load¶
The current through the load,
$$I_{load}=I_{norton}\cfrac{R_{norton}}{R_{norton}+R_{load}}$$
The voltage across the load,
$$V_{load}=I_{norton}\left(R_{norton}||R_{load}\right)$$