Superposition theorem
Introduction¶
In a linear time-invariant circuit with multiple voltage and current sources, the superposition theorem can be used to conveniently calculate the node voltage and branch current.
Definition¶
The superposition theorem states, " The total current in any part of a linear circuit equals the algebraic sum of the currents produced by each source separately. "
To find the current from Rload, we may apply the superposition theorem. The method is more intuitive and less complex than using KCL and KVL.
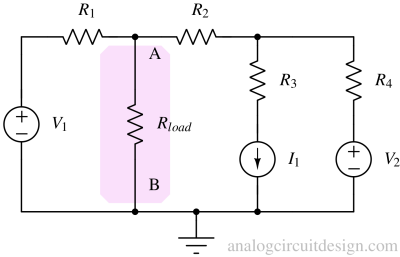
Keep only one power source "Turn on". "Turn off" all other power sources.¶
To make sure that only one power source is "on" at a time and the rest are turned off:
- We are replacing all other independent voltage sources with a short circuit (using a zero resistance wire).
- Replacing all other independent current sources with an open circuit (circuit break having infinite resistance).
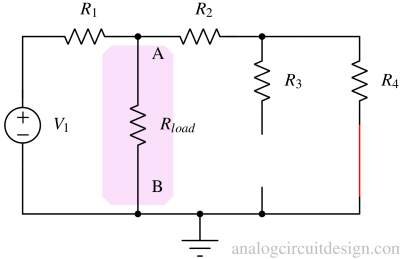
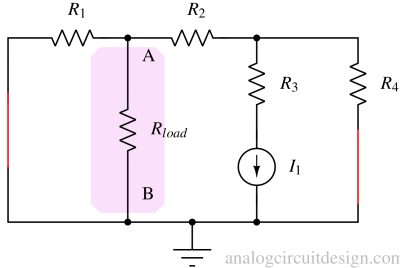
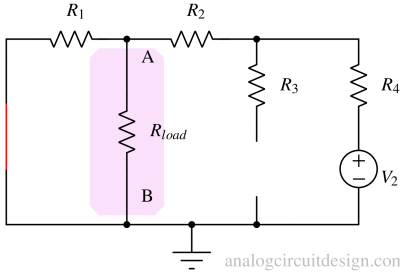
Calculate the current and voltage (with direction) because of all the sources¶
Current from Rload because of V1 from terminal A to terminal B (Fig. 2),
$$I_{V1}=\cfrac{V_1}{R_1+R_{load}||(R_2+R_4)}\cfrac{R_2+R_4}{R_{load}+R_2+R_4}$$
Current from Rload because of I1 from terminal A to terminal B (Fig. 3),
$$I_{I1}=-I_1\cfrac{R_4}{R_2+R_1||R_{load}}\cfrac{R_1}{R_1+R_{load}}$$
Current from Rload because of V2 from terminal A to terminal B (Fig. 4),
$$I_{V2}=\cfrac{V_2}{R_2+R_4+R_{load}||R_1}\cfrac{R_1}{R_{load}+R_1}$$
Superimpose the calculated currents and voltages together.¶
The current through Rload is (simply adding all the current obtained above with their sign) :
$$I_{load}=I_{V1}+I_{I1}+I_{V2}$$