Supply bypass capacitors¶
Power supply decoupling capacitors are commonly used to help filter out unwanted supply switching noise and act as a local supply for sensitive electronic components (e.g., high-frequency opamps and high-density digital ICs).
These supply decaps are placed as close as possible so that the parasitic wire inductance is as low as possible to the chip from where the supply decaps have been added.
Cause of voltage fluctuations¶
When an electronic component draws sharp (high frequency) current from the power supply, the wire inductances cause voltage drops. The wire inductance acts as very high impedances at high frequencies.
Local charge storage for switching circuits¶
Supply de-coupling capacitors act as local battery that provides the required current without letting the supply voltage drop.
However, these local batteries are not ideal. As we know, the voltage drops if a constant current is drawn out of a capacitor. The magnitude of voltage drop is inversely proportional to the capacitance.
Suppression of power supply noise¶
The decoupling capacitors form an LC low pass filter along with intentional ferrite beads (or inductors), which suppress the high-frequency switching noise of the power supply.
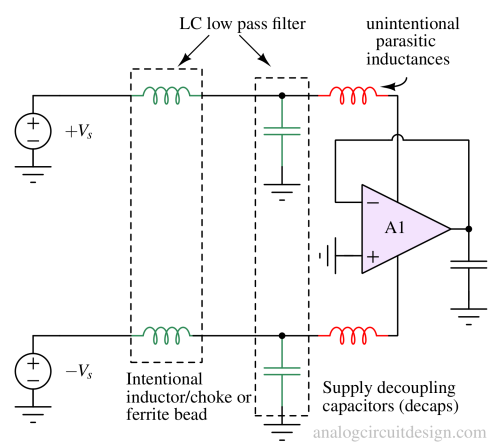
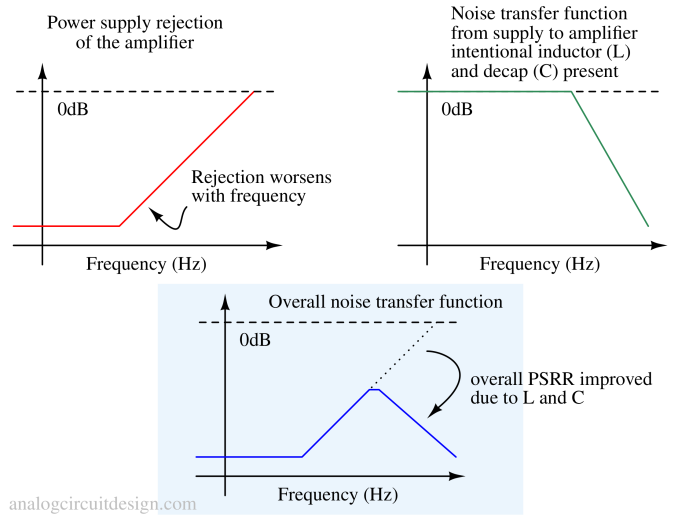
Having a well-designed decoupling capacitor network and an intentional inductor before the decoupling capacitor helps achieve good PSRR throughout the frequency range.
High-frequency stability of amplifiers¶
Parasitic inductance in the supply path may cause oscillation in high-frequency amplifiers. This is because the parasitic capacitances inside the chip no longer see a clean supply.
One end of those parasitic capacitances is connected to a signal node of the amplifier, while the other is now connected to the parasitic inductance of the board. This forms a parasitic LC tank which can severely degrade the amplifier's phase margin.
Effective series inductance¶
Every capacitor has a parasitic inductor (an effective series inductor, ESL). We need to choose capacitors having small effective series inductors. If ESL is very high, at high frequency, the capacitor may no longer behave as a capacitor but as an inductor.
The capacitors having very less ESL are called high-frequency capacitors.