Types of Capacitors¶
Capacitors come in many shapes, sizes, and dielectric materials, each suited for specific tasks based on their stability, voltage rating, and frequency response. It is crucial to know about each capacitor for achieving optimal circuit performance.
Classification based on polarization¶
Based on polarization of terminals, capacitors are divided into two categories :
Polarized capacitors¶
A polarized capacitor is also termed an electrolytic capacitor. These capacitors are used to achieve high capacitive density. These cannot tolerate reverse voltage. These are mostly used in DC circuits where the polarity is by design fixed. Aluminium electrolytic capacitors, Tantalum capacitors are example of polarized capacitors.
Unpolarized capacitors¶
Unpolarized capacitors don't get destroyed by reverse voltage and can be used in pure AC circuits. The capacitor density may not be very high. Very low value of capacitance can be achieved. Ceramic capacitors are unpolarized capacitors.
Ceramic capacitors¶
These capacitors use a ceramic material as the dielectric between the plates. They are small, inexpensive, and have a wide range of capacitance values. However, they can have higher levels of parasitic effects, making them less suitable for high-frequency applications. These can generate piezoelectric noise (mechanical stress to electrical noise).
Table : Ceramic Dielectric Classes
| Class | Examples (EIA Code) | Material Type | Temperature Sensitivity/Stability (TCC) | Capacitance Range | Capacitance Volumetric density | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | C0G (NP0), C0H, C0K | Non-ferroelectric ceramics (low-loss) | Very stable (<30 ppm/°C) | Low (pF to nF range) | Low | Frequency control, RF circuits, precision timing (e.g., radio, TV tuners) |
| Class II | X7R, X5R, Y5V, Z5U | Ferroelectric ceramics (barium titanate-based) | Moderate stability (±15% or more) | Medium to high | High | General decoupling, filtering, power supply bypassing |
| Class III | Z5U, Y5V | High-permittivity ceramics (ferroelectric) | Poor stability (large variation) | Very high (µF range) | Very High | Bulk capacitance, low-frequency filtering (when precision is not critical) |
Multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs)¶
These are compact capacitors (SMD footpr\int) with multiple layers of ceramic material and metal electrodes. Small parasitic inductance gives better high-frequency performance compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors. It has better stability over temperature, depending on the temperature coefficient.
MLCCs are made of alternating layers of metallic electrodes and dielectric ceramics.
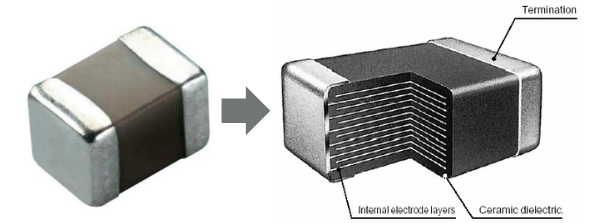
Ceramic disc capacitors¶
Ceramic disc capacitors are manufactured by coating a ceramic disc with silver contacts on both sides. To achieve larger capacitances, these devices can be made from multiple layers. MLCCs are now preferred over ceramic in compact PCBs because usually, ceramic disc capacitors have larger sizes. Ceramic disc capacitors have mostly through hole PCB footpr\int.

Electrolytic capacitors¶
Aluminium electrolytic capacitors¶
These capacitors use an aluminum oxide layer as the dielectric. These types of capacitors provide a much higher level of capacitance for a given volume than most ceramic capacitors. Also, these are budget-friendly.

The typical capacitance ranges from 4.7uF to 680uF. The tolerance is 10%-20%. The voltage ratings ranges from 10VDC to 35VDC. Usually, for same capacitance, the size of capacitor grows with voltage.
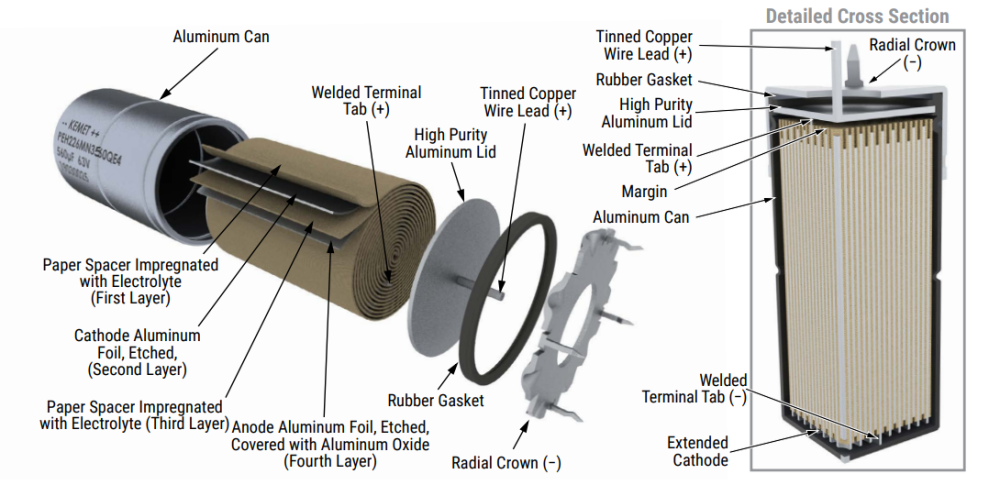
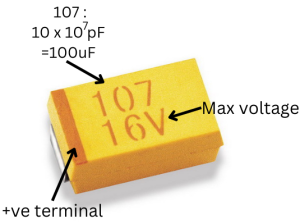
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors¶
Tantalum capacitors use tantalum pentoxide as the dielectric. They are smaller and have lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to aluminum electrolytic capacitors, making them suitable for applications requiring low ESR and tight tolerances.
Tantalum capacitors do not change capacitance with applied DC bias. These do not suffer from mechanical stress or piezoelectric effect.
Comparison table between ceramic and electrolytic capacitor¶
| Important parameters | Ceramic | Aluminium electrolytic | Tantalum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ESR and ESL | Lowest | Highest | Moderate |
| 2 | Capacitance density | Low | High | Highest |
| 3 | Temperature range | Moderate | High | Highest |
| 4 | DC bias dependent capacitance | Worst | Moderate | Good |
| 5 | Piezoelectric | Sensitive | Insensitive | Insensitive |
| 6 | High frequency filtering | Best | Worst | Good |
Film capacitors¶
Film capacitors, also known as polymer film capacitors, are electrical capacitors utilizing an insulating plastic film as the dielectric. The dielectric film materials vary depending on the required dielectric strength, primarily Polypropylene (PP), Polyester (PET), Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), etc. The electrodes could be metalized aluminum, zinc, or Al-Zn alloy applied directly to the surface of the plastic film.
It has a nearly infinite shelf life. It has the ability to withstand power surges without damage and offers a very low self-inductance (ESL) and very low self-resistance (ESR).
Polyster/Mylar film capacitors¶
The polyester dielectric used in these capacitors also referred to as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offers a high dielectric strength. This means that high-voltage capacitors can be made relatively small. For reference, a Polyster capacitor with capacitance of 4.7uF can have voltage ratings of 400V with 10% tolerance.

Polypropylene film capacitors¶
In these capacitors, the di-electric is made of polypropylene (PPN) and electrodes are made up of aluminium. It usually has self-healing properties.
These offer excellent stability and low-loss characteristics, making them suitable for DC blocking, bypass, coupling, and temperature compensation. For reference, a polypropylene capacitor can have capacitance range from 0.1-10uF with tolerance ranging from 10%-20%. The voltage range supported is ~600VDC.

Variable capacitors¶

These capacitors have adjustable capacitance and are often used in tuning circuits, such as in radios or oscillators. There are mechanically controlled and electronically controlled capacitors. Electronically controlled capacitors are used for voltage-controlled oscillators.
Supercapacitors¶
These are high-capacity capacitors that can store much more energy than traditional capacitors. These are intolerant to reverse bias. They have fast charge and discharge times and are used for energy storage and burst power applications. For example: a supercapacitor which have a capacitance value of 200F, has a voltage rating of 3V. The ESR is 4.5mΩ. Capacitance tolerance is 5% to 20%. The continuous current is in Amperes. The energy storage is 0.35Wh.
To learn more about supercapacitors, visit this page: Supercapacitors

Mica capacitors¶
These capacitors use mica as the dielectric material and are known for their stability and high precision. They are often used in applications requiring tight tolerances and low losses.
Paper capacitors¶
These capacitors use paper as the dielectric material. They were commonly used in older electronics but have largely been replaced by more modern types.